Planet Generation Tools User Manual
Planet Generation Tools Overview
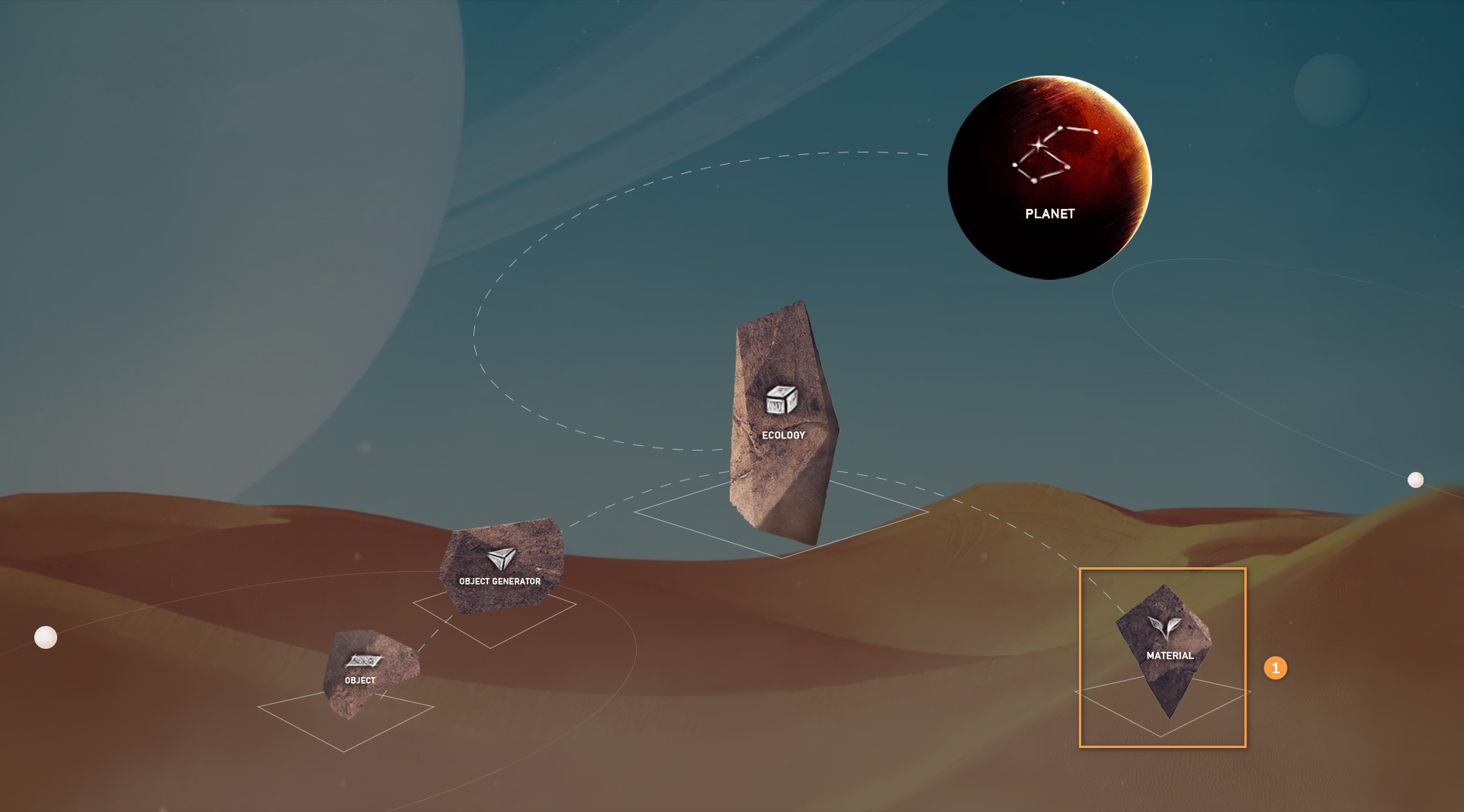
Current structure of planet data:
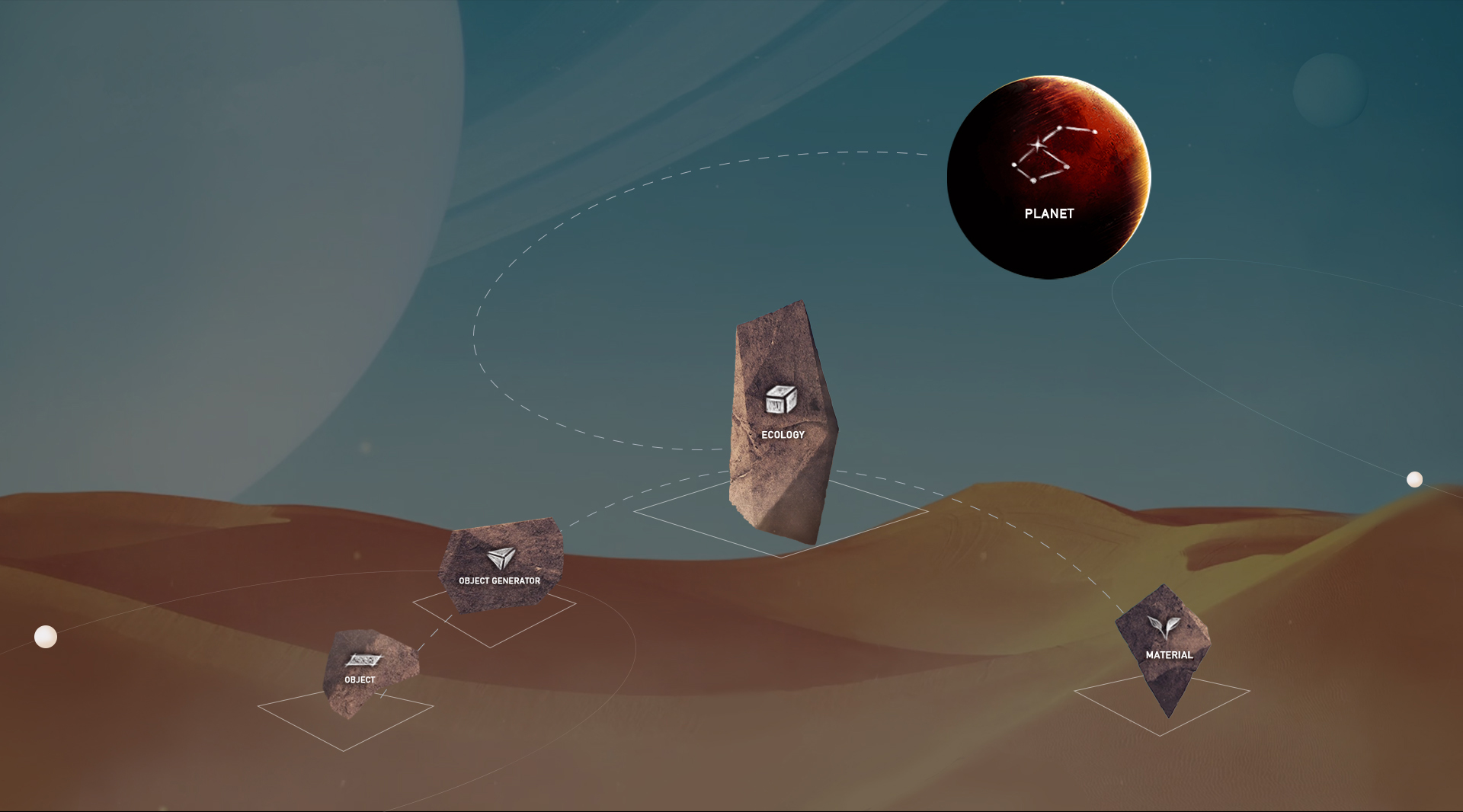
Planet Generating Tools (the Voxel Editor) Overview:
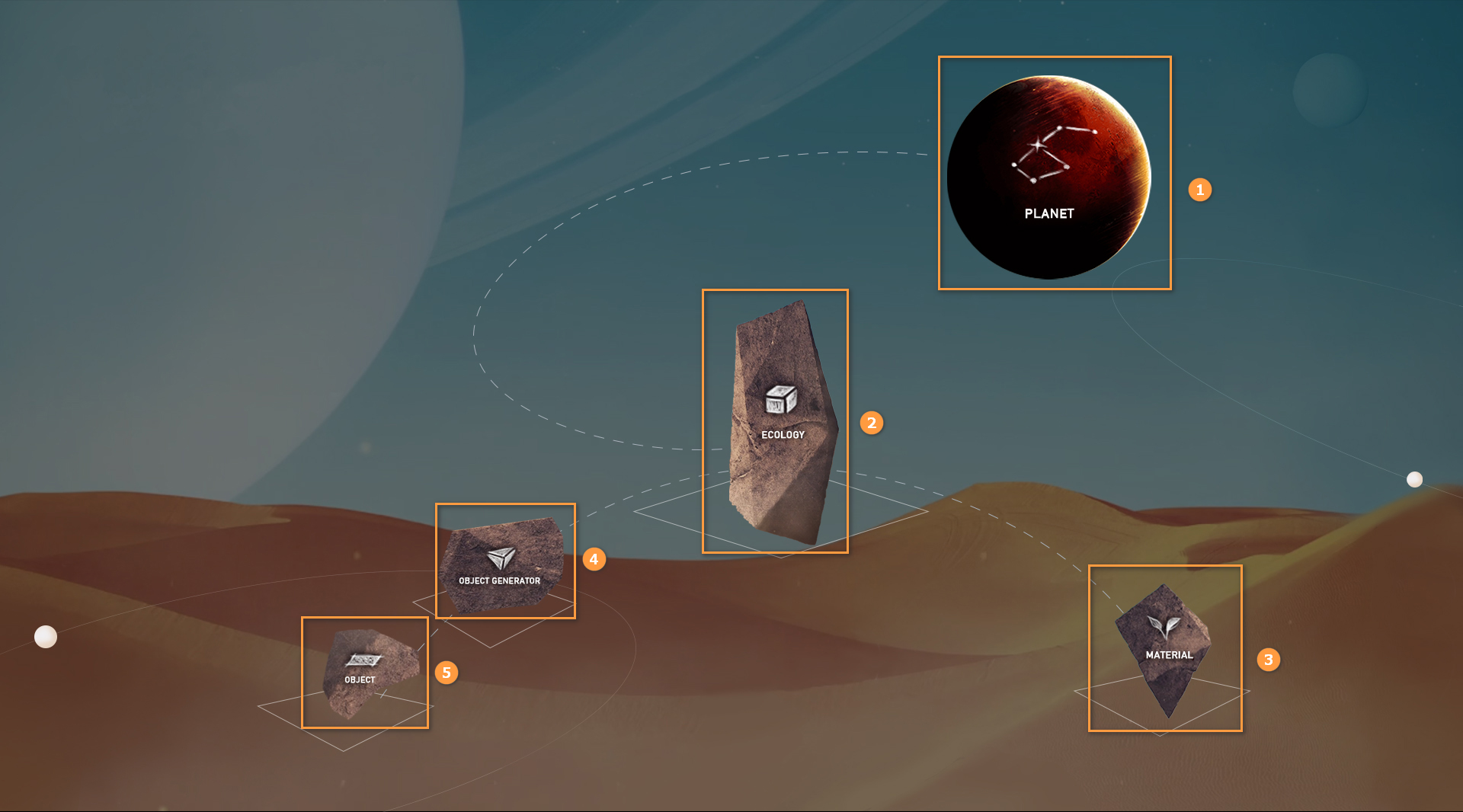
| No. | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | PLANET |
| 2 | ECOLOGY |
| 3 | MATERIAL |
| 4 | OBJECT GENERATOR |
| 5 | OBJECT |
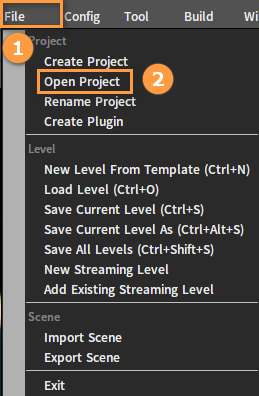
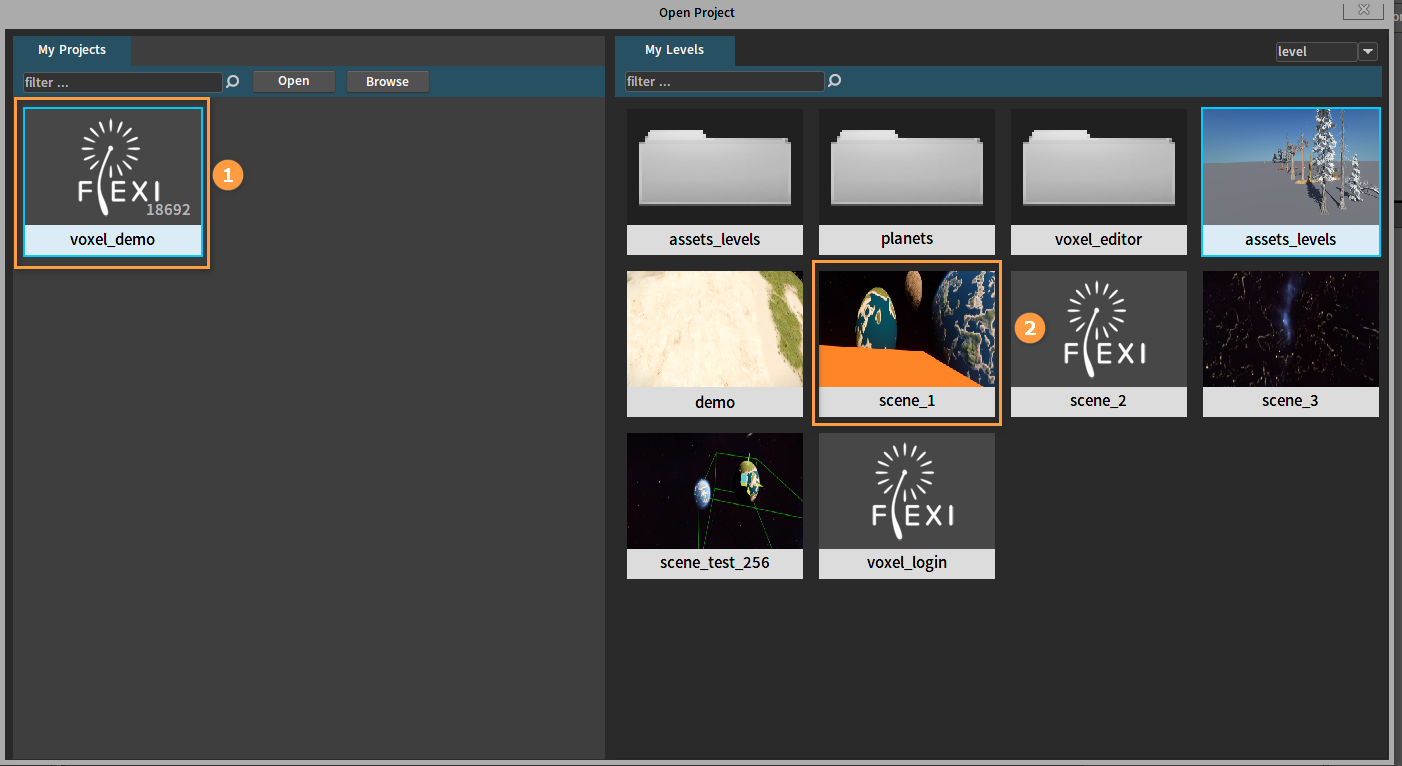
Opening Projects
Open the Editor and click File -> Open Project.
Click the Browse button to select a project to open.
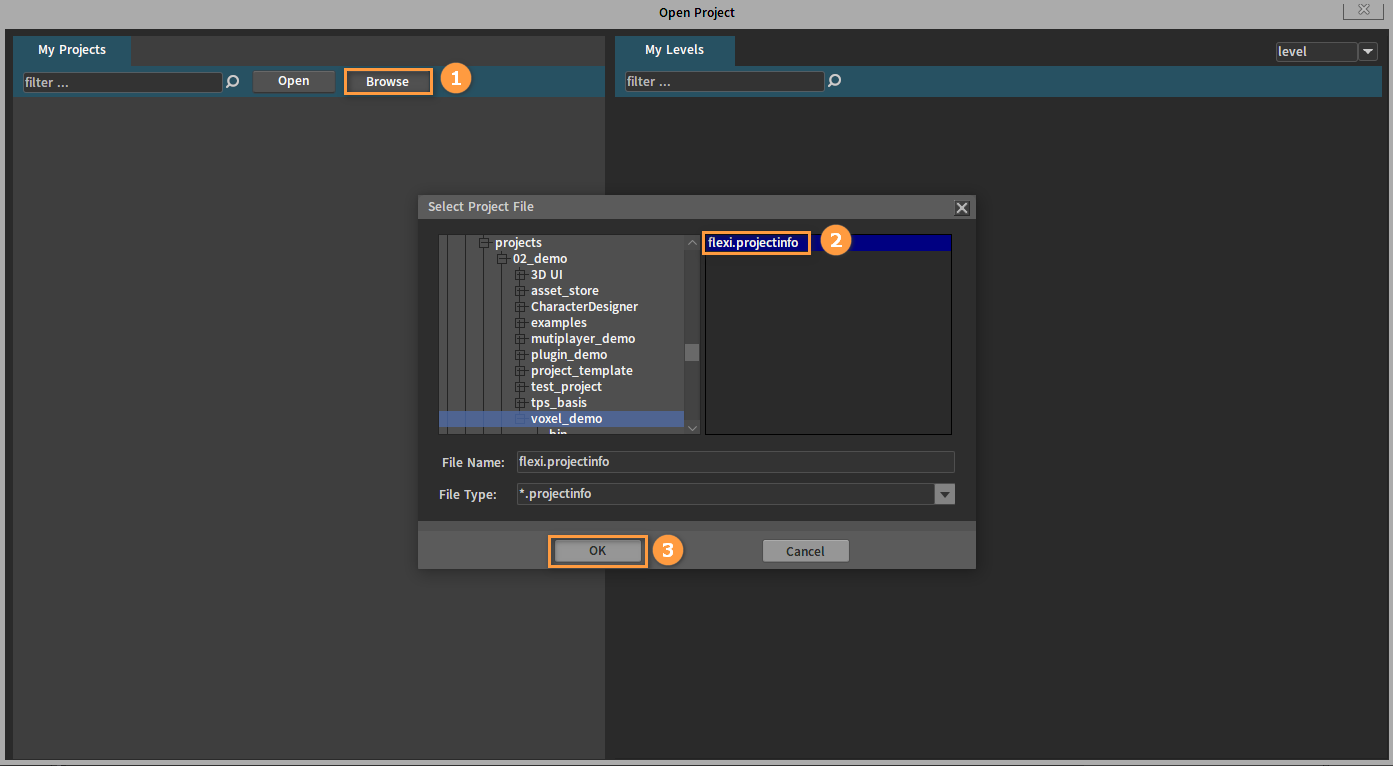
Select a level and double-click to enter it.
Editing Planets
Opening Planets
Click Tool -> Voxel Editor to open the Voxel Editor.
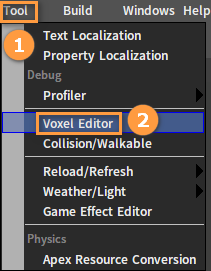

In the Voxel Editor, click PLANET to open the Planet Editor.

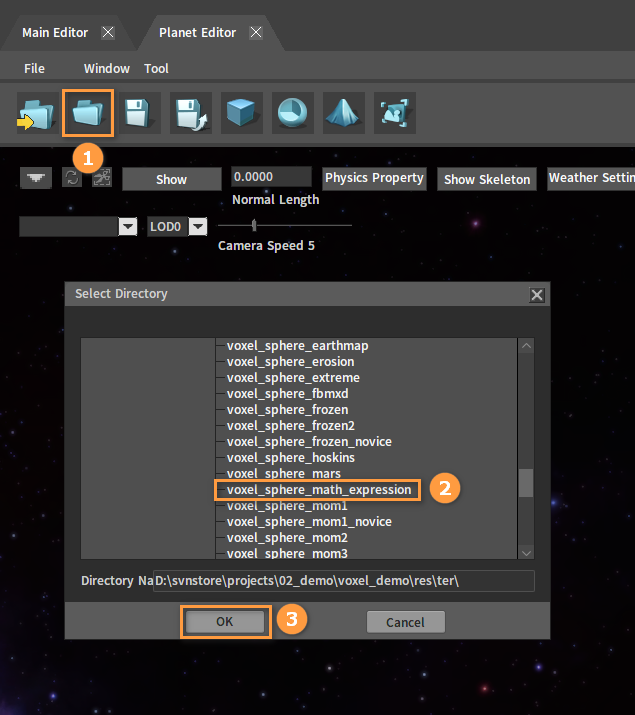
In the Planet Editor, click the Open button, select a planet and open it for editing.
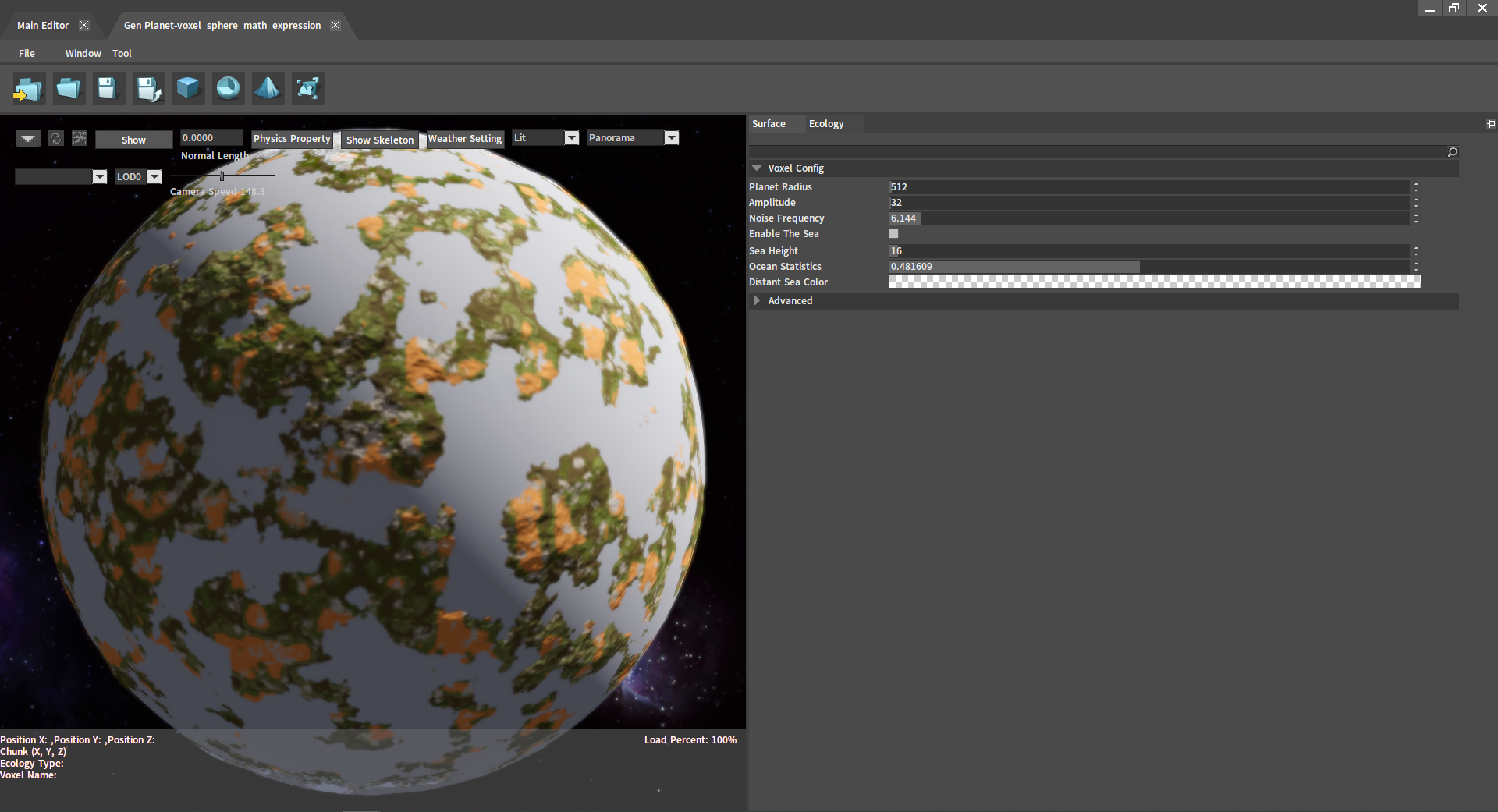
Planet Properties
Surface
In the Surface panel of the Planet Editor, various surface properties of the planet can be modified.
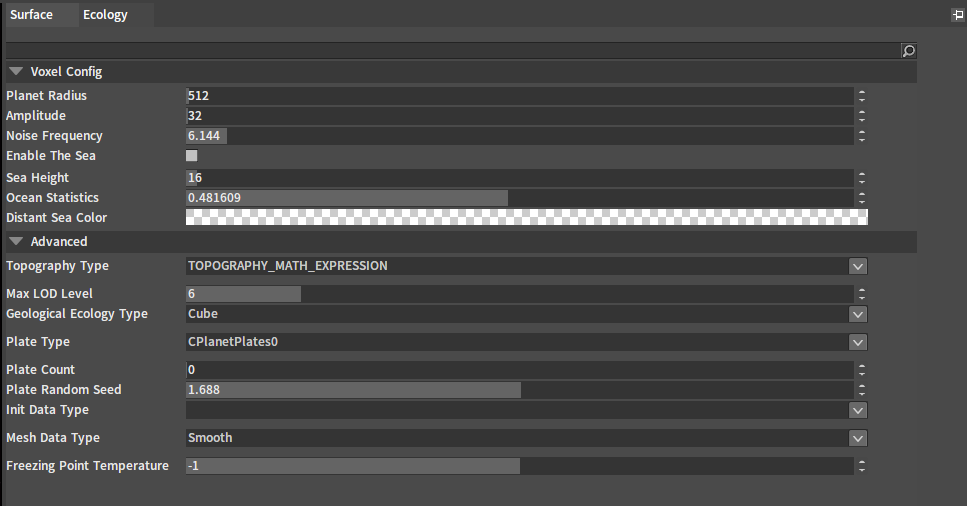
| Setting | Property | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Voxel Config | Planet Radius | Planet radius. |
| Amplitude | The relief of terrain. | |
| Noise Frequency | The density of mountains within a certain range. | |
| Enable The Sea | Whether the planet has seas. | |
| Sea Height | Sea height. | |
| Ocean Statistics | Ocean-to-land ratio. | |
| Distant Sea Color | Sea color in a distant view. | |
| Advanced | Topography Type | Control topographical features of the planet. |
| Max LOD Level | Maximum number of LOD levels. | |
| Geological Ecology Type | Geological ecology type (e.g. Cube is a cube generated from 3 dimensions, Soil Infertility, Temperature and Humidity). | |
| Plate Type | Plate type. | |
| Plate Count | Plate count. | |
| Plate Random Seed | The location of each plate control point used to generate. | |
| Init Data Type | Voxel scene type. | |
| Mesh Data Type | Mesh data type. | |
| Freezing Point Temperature | Control whether ecology, mountains or sea water, etc. are frozen (e.g. If the temperature of the sea is below this value, then it will become a glacier). |
Ecology
In the Ecology panel of the Planet Editor, the ecology on the planet can be edited.
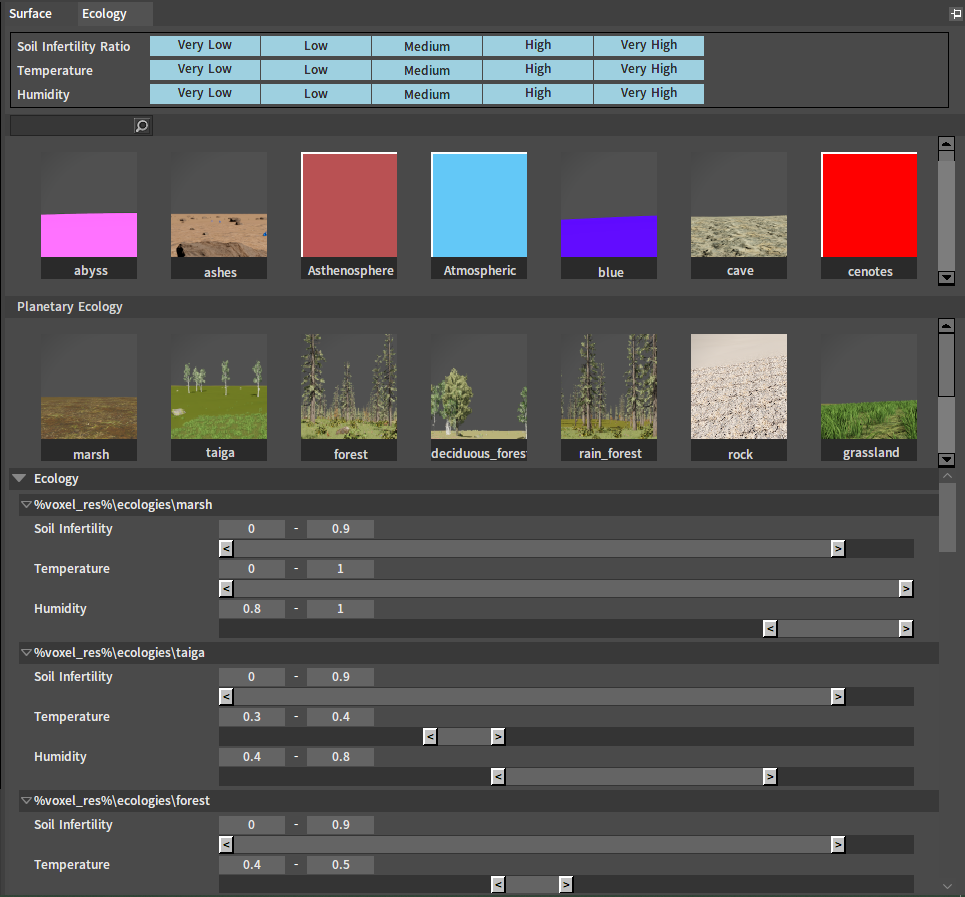
Drag the ecology into the blank space of Planetary Ecology to add it to the planet.
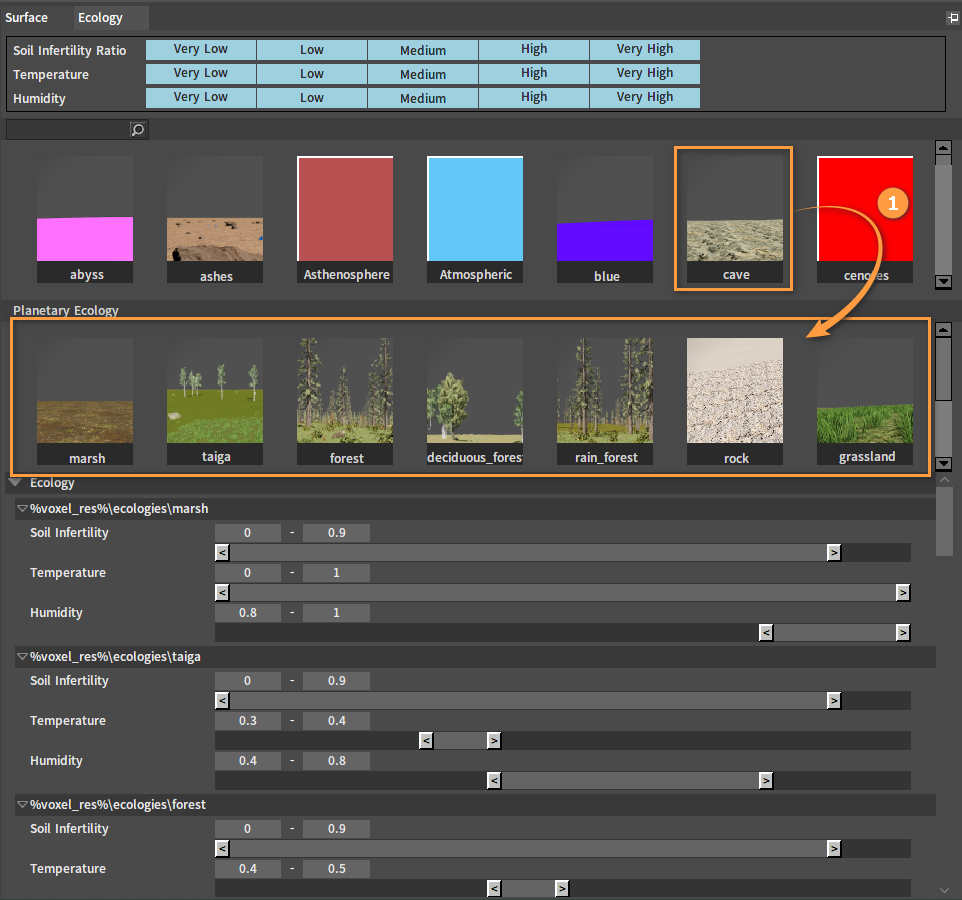
Select an ecology in Planetary Ecology, modify its Soil Infertility, Temperature and Humidity value ranges, then click the Generate button, and the planet will redistribute the ecology according to the modification.
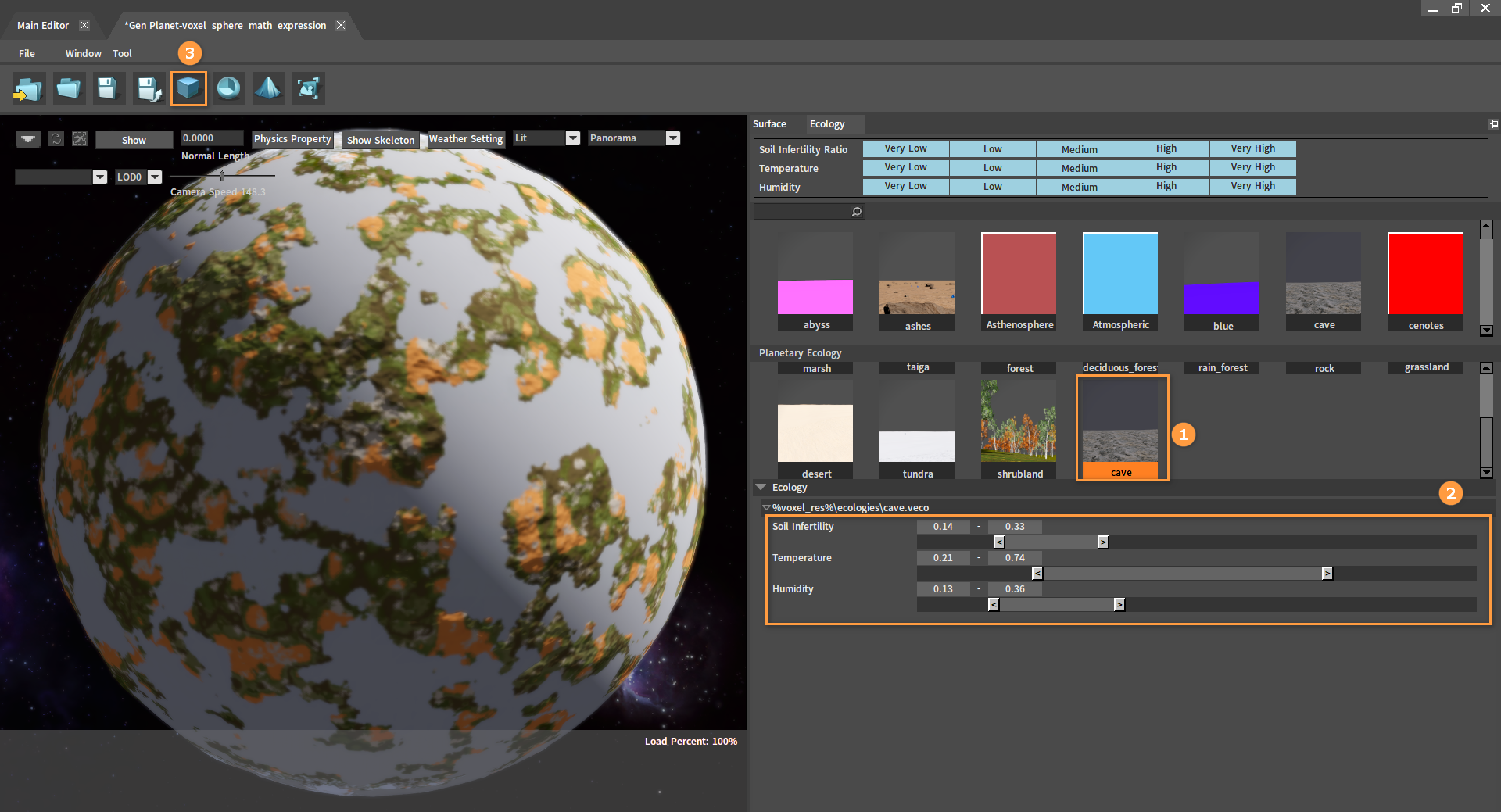
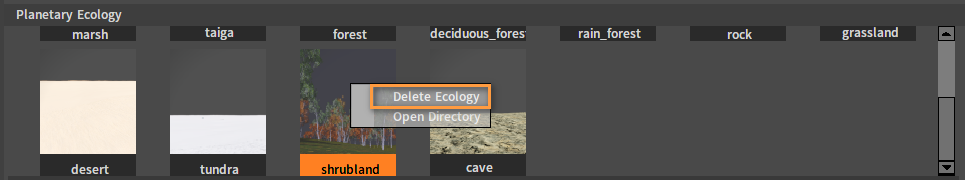
In Planetary Ecology, right-click on ecology and select Delete Ecology to delete it.
Editing Planetary Rings
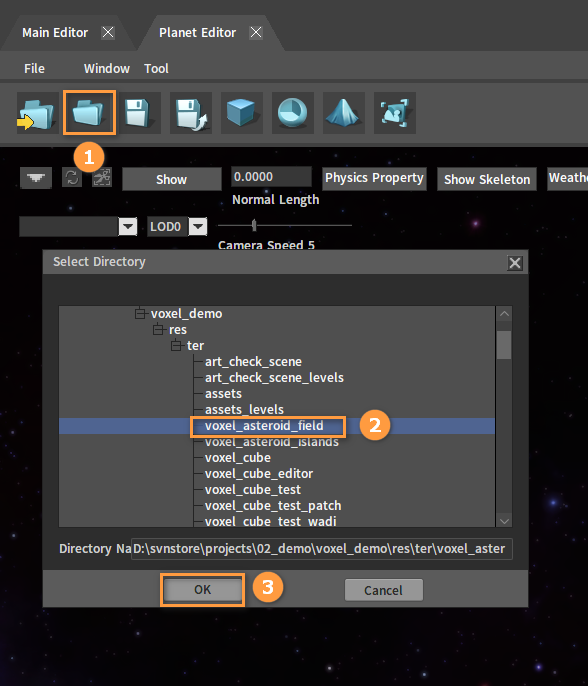
In the Planet Editor, click the Open button, select a planetary ring and open it for editing.
The properties of the planetary ring can be modified in the Planetary Ring panel.
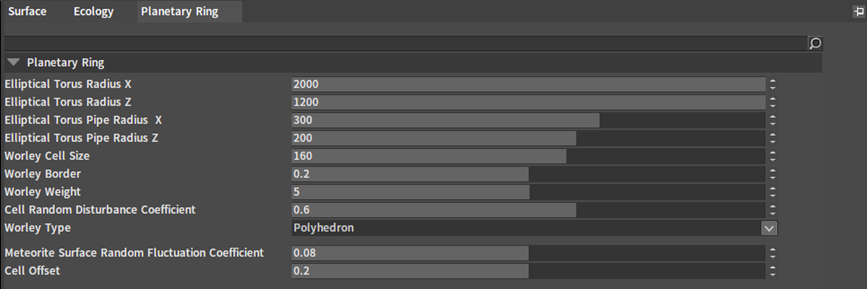
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Elliptical Torus Radius X | Length of the whole elliptical torus. |
| Elliptical Torus Radius Z | Width of the whole elliptical torus. |
| Elliptical Torus Pipe Radius X | Thickness of the elliptical torus pipe. |
| Elliptical Torus Pipe Radius Z | Width of the elliptical torus pipe. |
| Worley Cell Size | The larger the value, the larger the generated meteorite; the smaller the value, the more fragmented the meteorite. |
| Worley Border | Determine the threshold of the meteorite border. |
| Worley Weight | Control the voxel value. |
| Cell Random Disturbance Coefficient | Random disturbance coefficient of the generated cell (0~1), 0 means the cell has no random disturbance, i.e., the cube. |
| Worley Type | Control the shape of the meteorite. |
| Meteorite Surface Random Fluctuation Coefficient | Random fluctuation coefficient of the meteorite surface, the larger the value, the more obvious the fluctuation. |
| Cell Offset | Random offset coefficient of meteorite border values, which allows scaling of the meteorite. |
Other Features
After opening a planet, click Tool -> Rotation Speed to set the planet rotation speed.
Click Tool -> Preview Mode to turn on or off the Preview Mode.
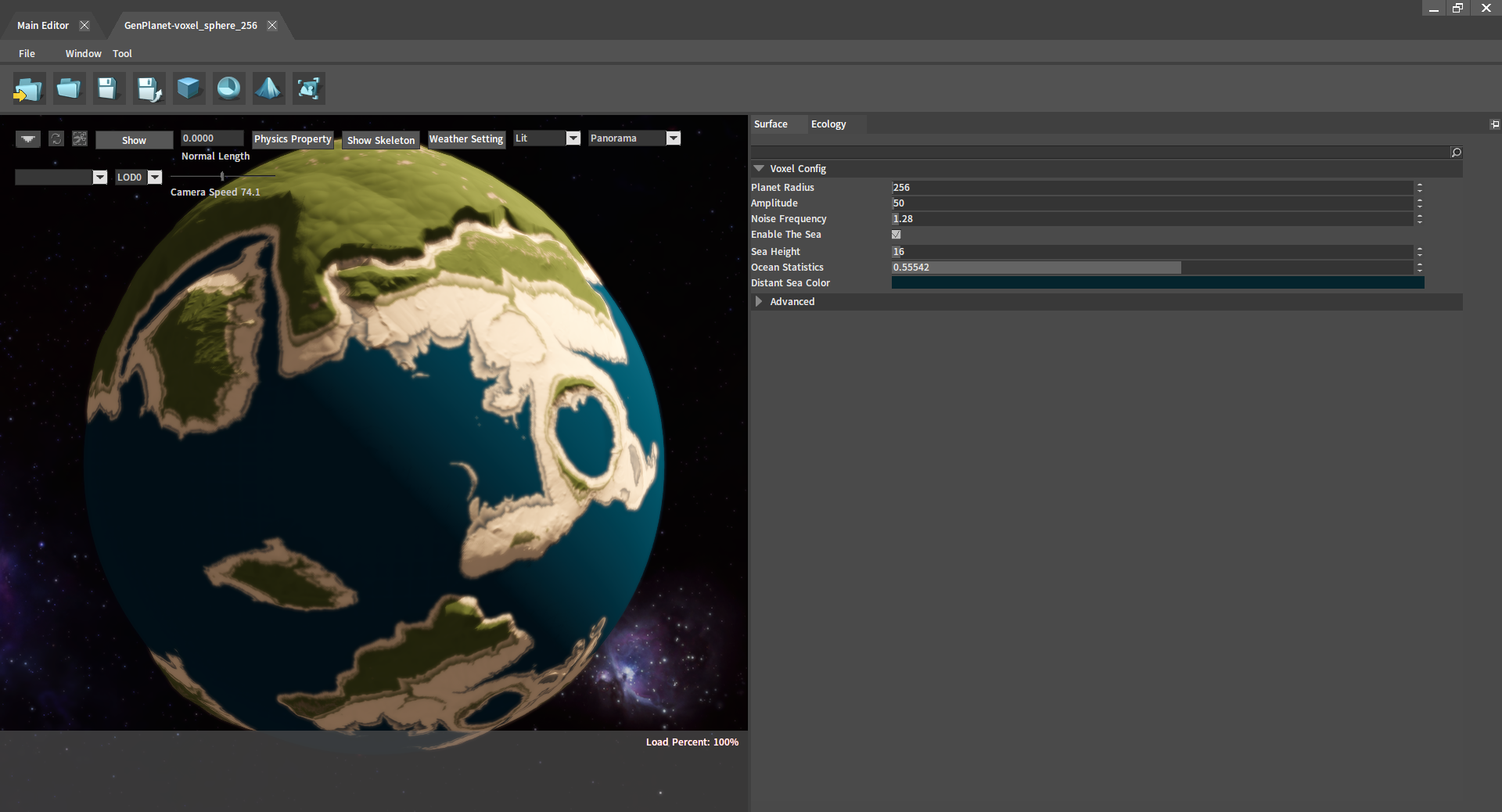
Turn on the Preview Mode:
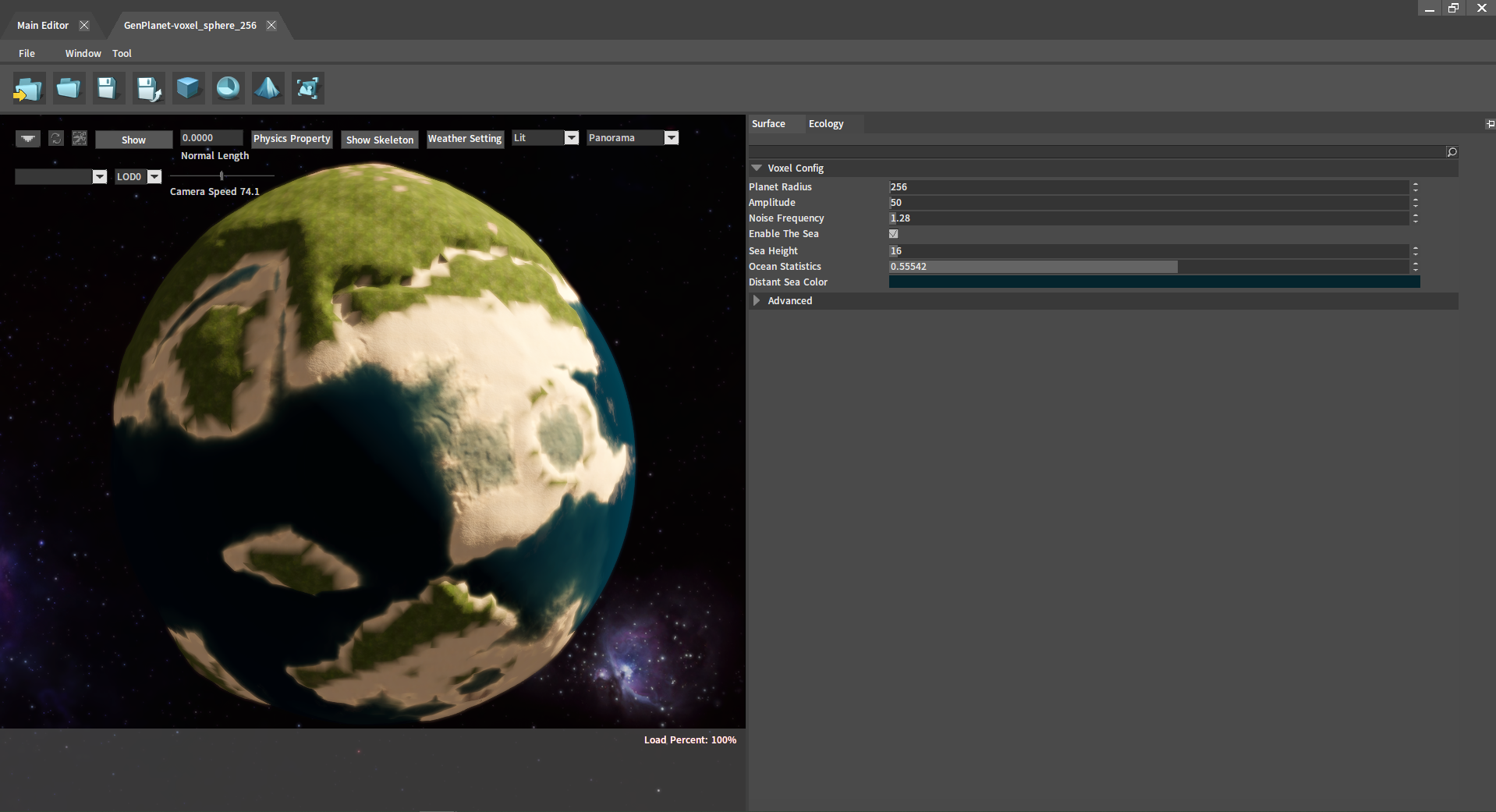
Turn off the Preview Mode:
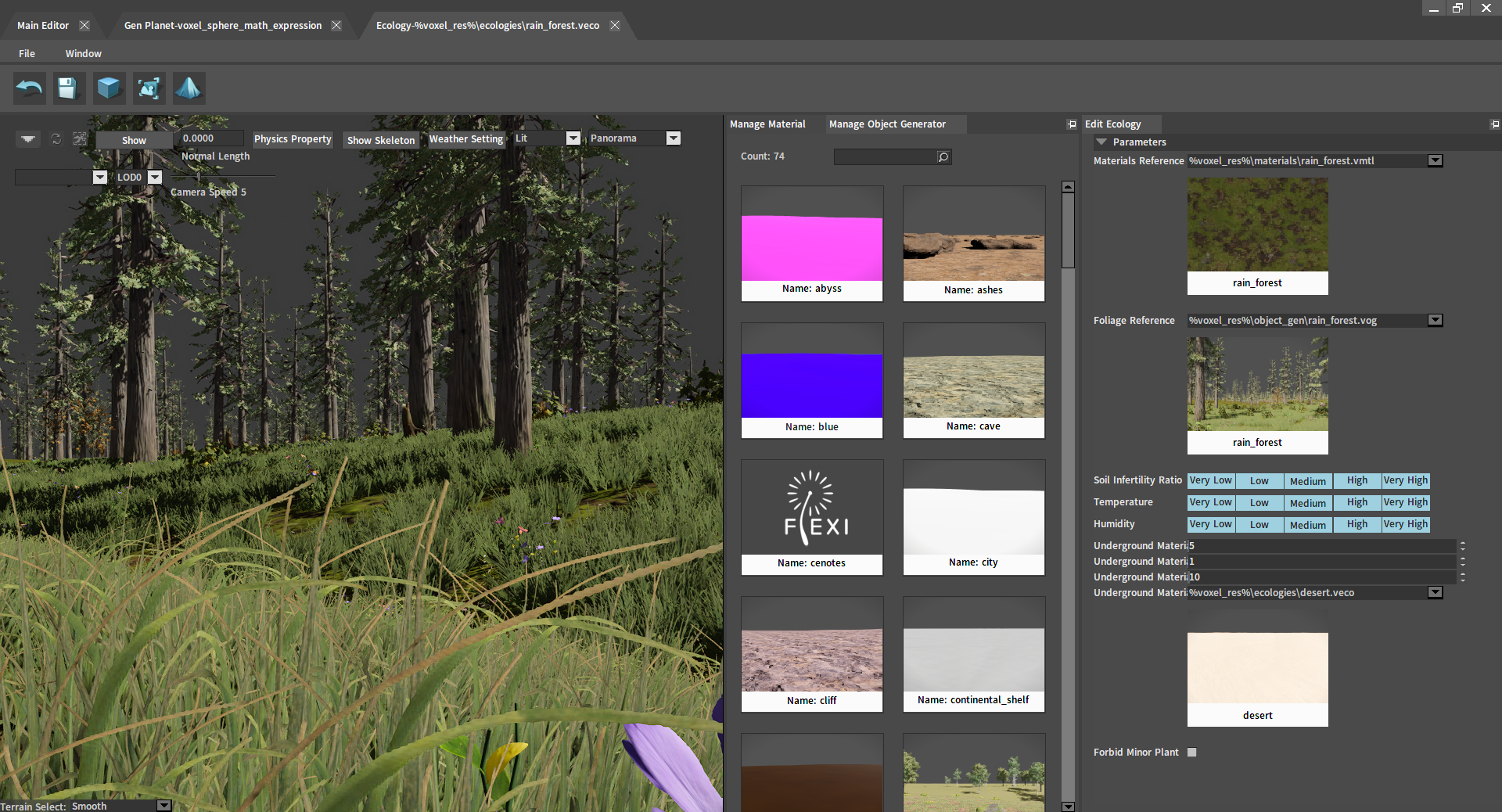
Editing Ecologies
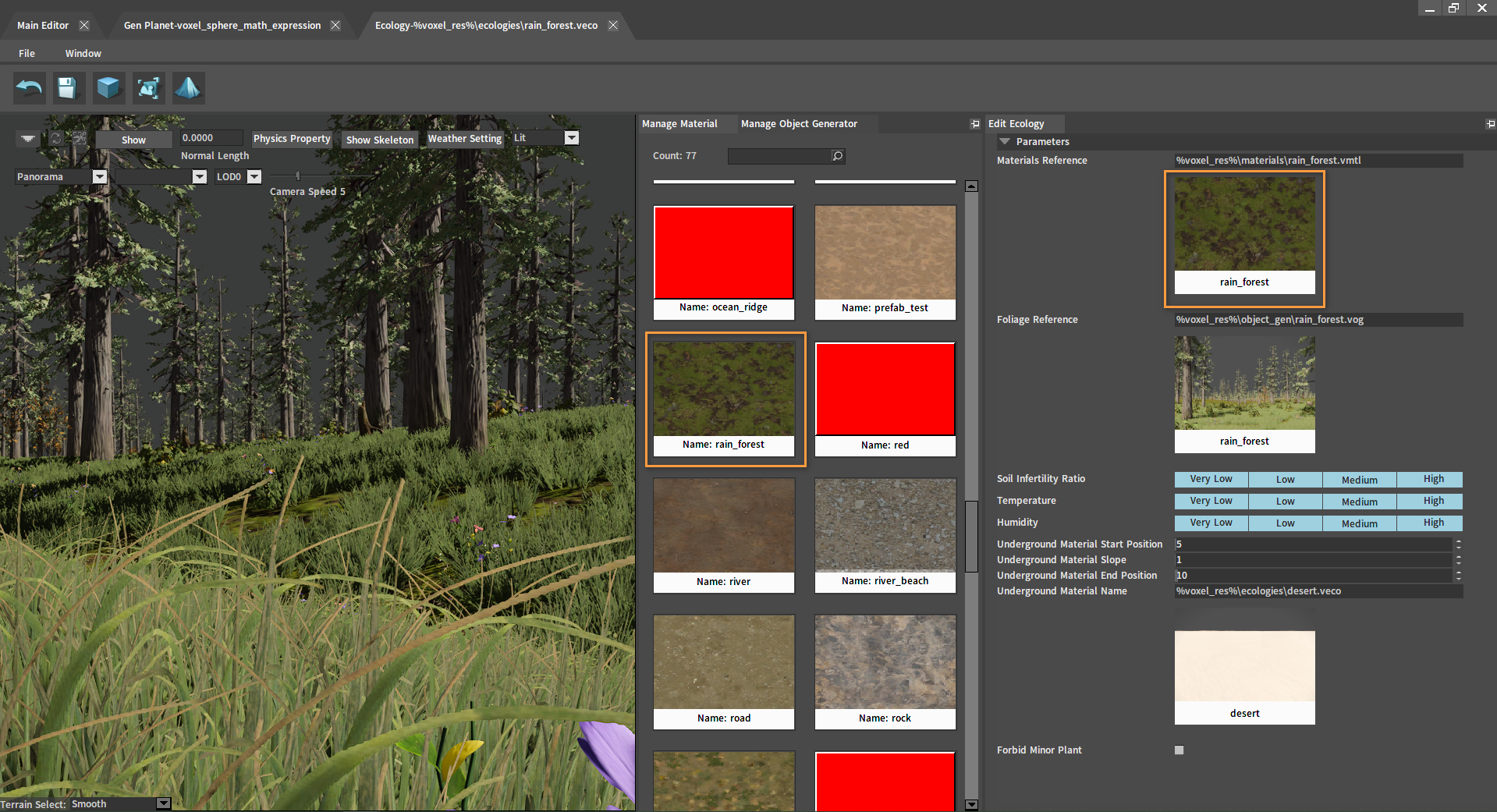
Double-click the ecology under Planetary Ecology in the Planet Editor to enter its editing interface. Or click ECOLOGY from the main interface of the Voxel Editor to open the Ecology Editor, and double-click the ecology to enter the editing interface.
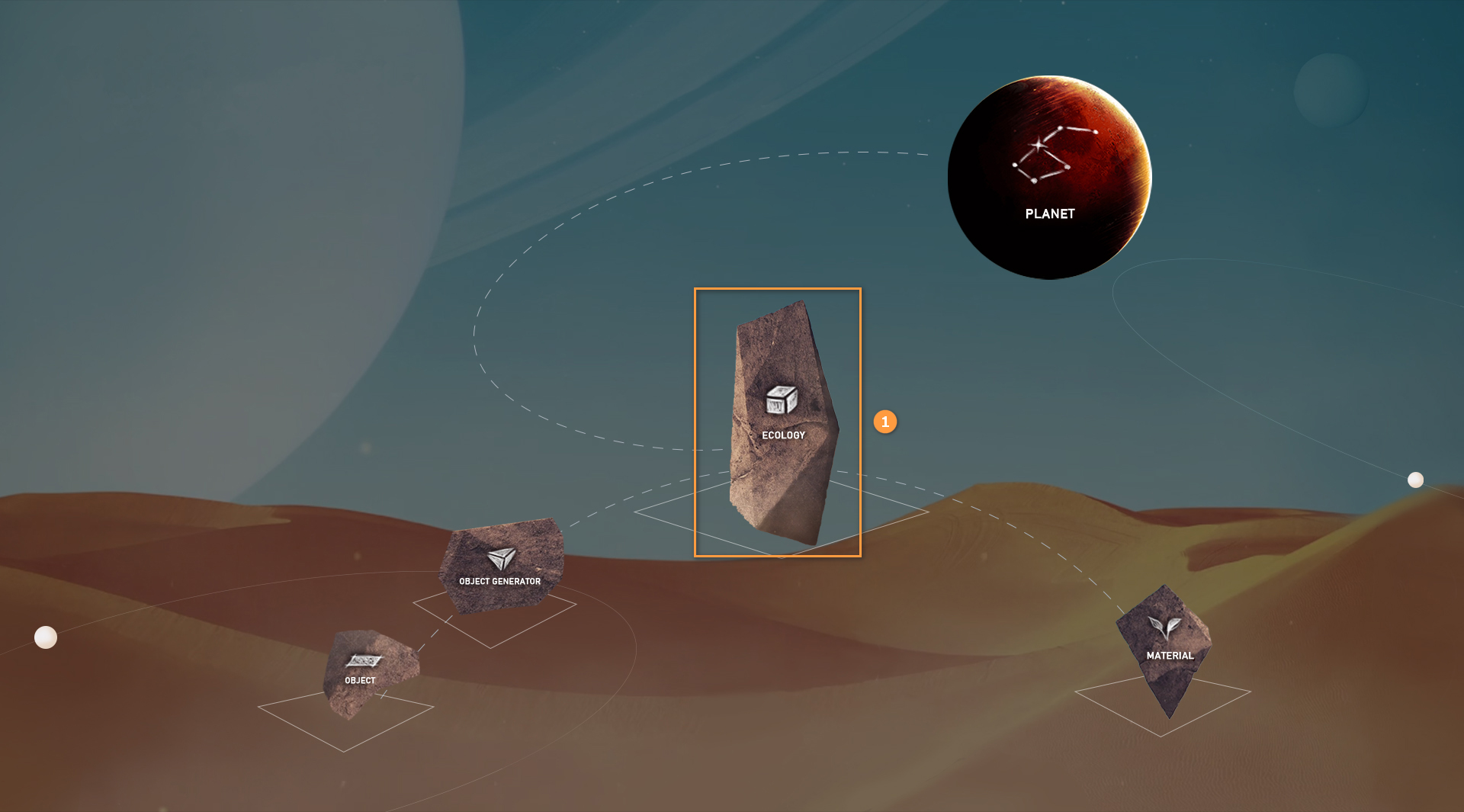
Enter the Ecology Editor interface from the main interface of the Voxel Editor:
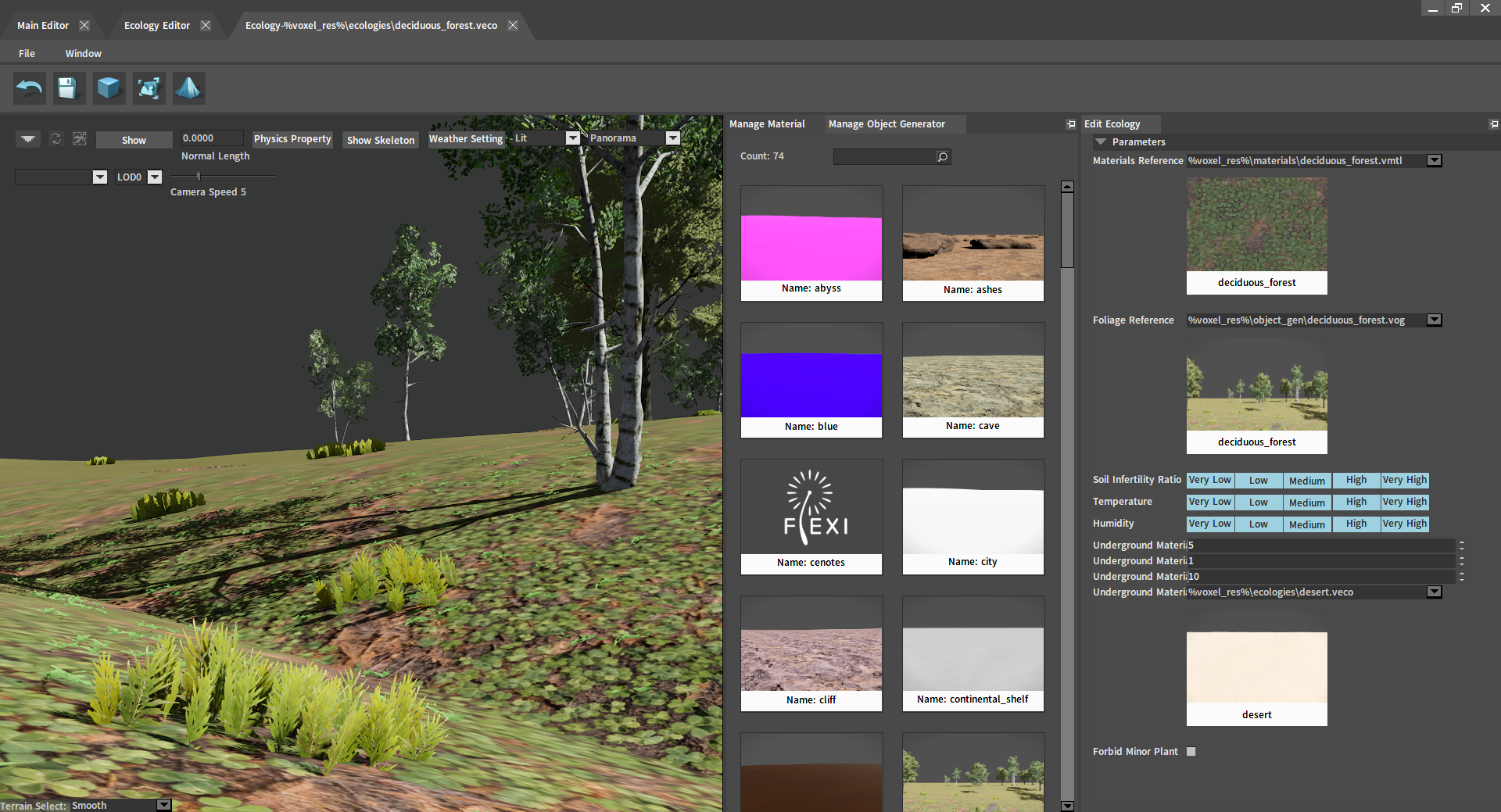
Various properties of the ecology can be modified in the Edit Ecology panel.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Materials Reference | Select the surface material of the ecology. |
| Foliage Reference | Select the object generator of the ecology. |
| Soil Infertility | Filter materials and object generators by soil infertility. |
| Temperature | Filter materials and object generators by temperature. |
| Humidity | Filter materials and object generators by humidity. |
| Underground Material Start Position | Affect the blend of the original ecology and underground materials. |
| Underground Material Blend | Affect the blending relationship of underground material ecologies. |
| Underground Material End Position | Affect the blend of underground and deep underground material ecologies. |
| Underground Material Name | Select underground materials. |
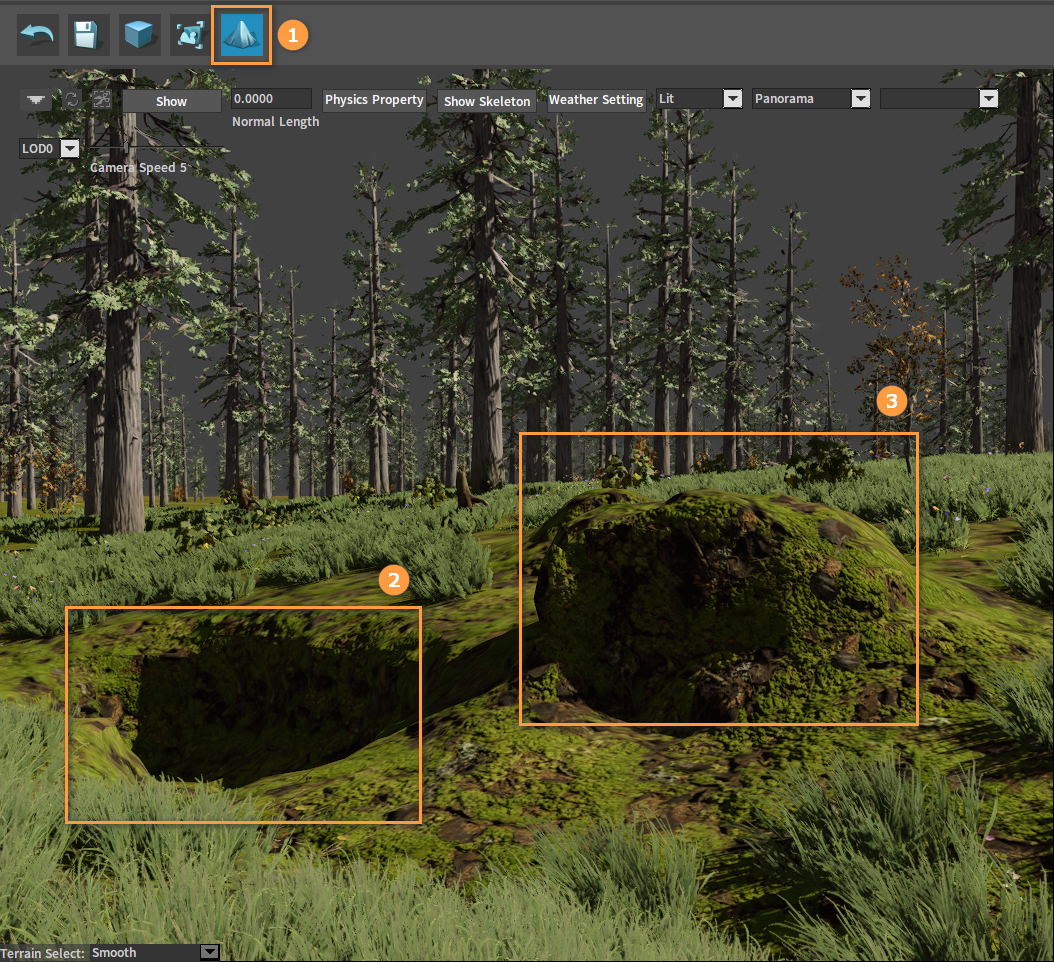
Click the Scene Edit button. Left-click the surface to dig down, and Ctrl + Left-click to fill up the surface.
Editing Materials
Double-click the Material Reference or the material under the Manage Material in the Ecology Editor to enter its editing interface. Or click MATERIAL from the main interface of the Voxel Editor to open the Material Editor, and double-click the material to enter its editing interface.
Enter the Material Editor interface from the main interface of the Voxel Editor:
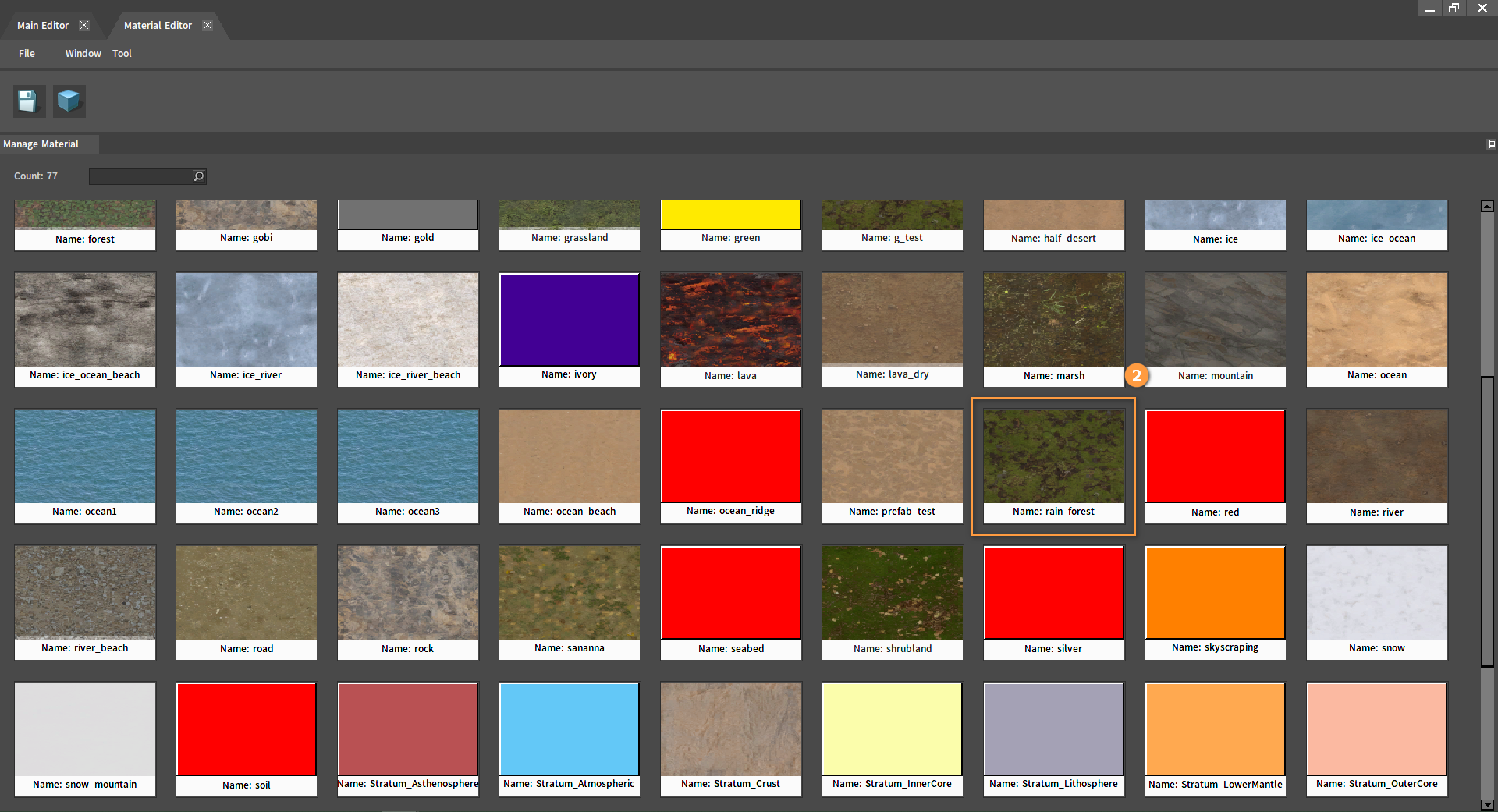
Various properties of the material can be modified in the Edit Material panel.
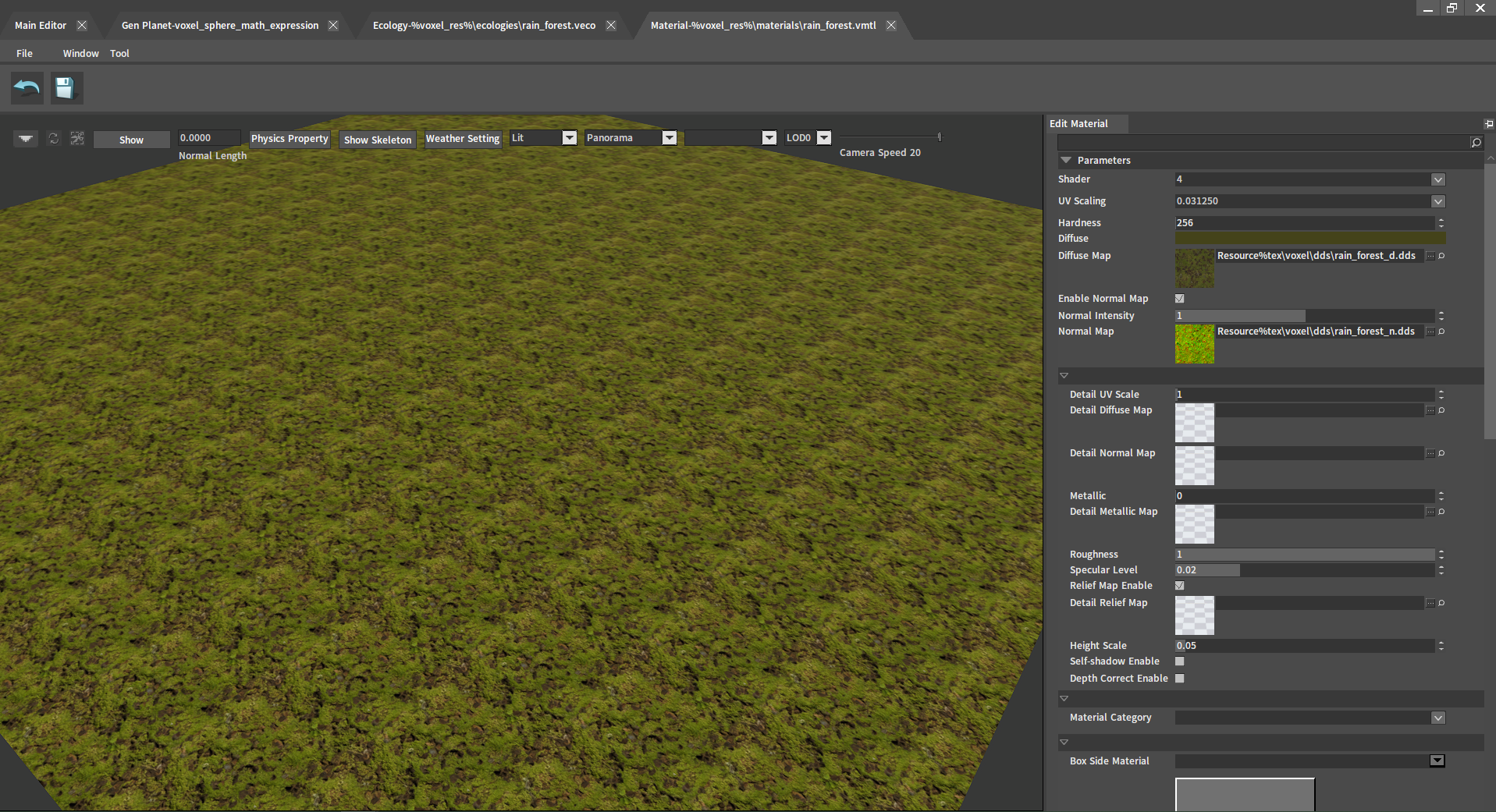
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Shader | Rendering levels used by this material (the larger the value, the higher the rendering accuracy). |
| UV Scaling | Equal scaled texture UV. |
| Hardness | Hardness. |
| Diffuse | Diffuse color. |
| Diffuse Map | Diffuse map. |
| Enable Normal Map | Enable normal map. |
| Normal Intensity | Texture details of the material (The larger the value, the higher the LODs). |
| Normal Map | Normal map. |
| Detail UV Scale | Detail UV scale. |
| Detail Diffuse Map | Detail diffuse map. |
| Detail Normal Map | Detail normal map. |
| Metallic | Metallic. |
| Detail Metallic Map | Detail metallic map. |
| Roughness | Roughness. |
| Specular Level | Specular level (The higher the value, the more obvious the light reflected by the material). |
| Enable Relief Map | Enable relief map. |
| Detail Relief Map | Detail relief map. |
| Height Scale | Relief map height scale. |
| Enable Self-Shadow | Enable relief map self-shadow. |
| Enable Depth Correct | Enable relief map depth correct. |
| Material Category | Material category. |
| Box Side Material | Box side material. |
| Box Bottom Material | Box bottom material. |
Editing Object Generators
Go back to the Ecology Editor interface, double-click the Foliage Reference or the object generator under the Manage Object Generator to enter its editing interface. Or click OBJECT GENERATOR from the main interface of the Voxel Editor, and double-click an object generator to enter its editing interface.

Enter the Object Generator interface from the main interface of the Voxel Editor:

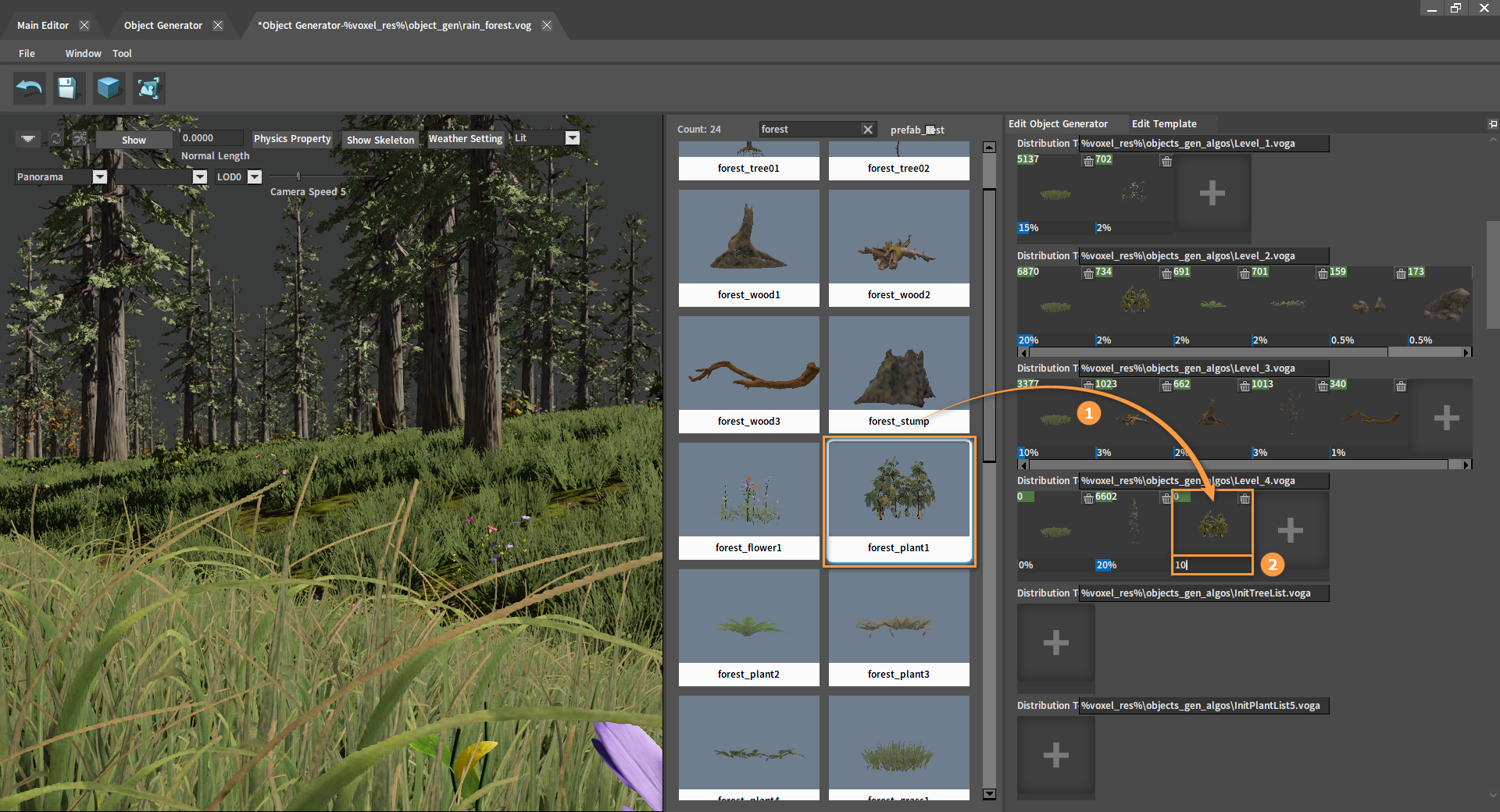
In the Object Generator, you can add or delete objects, and modify the object spawn density and distribution range.
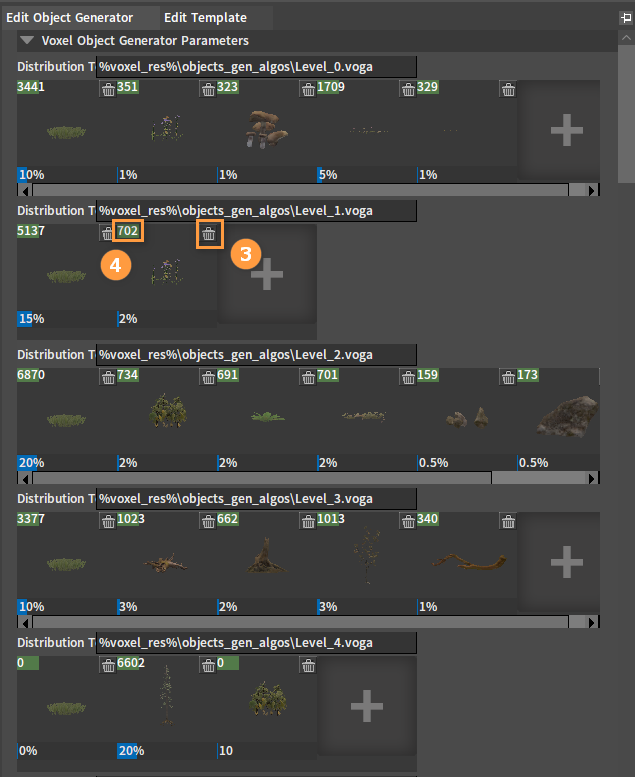
Click the Plus button at the bottom of the Edit Template panel to add different distribution templates.
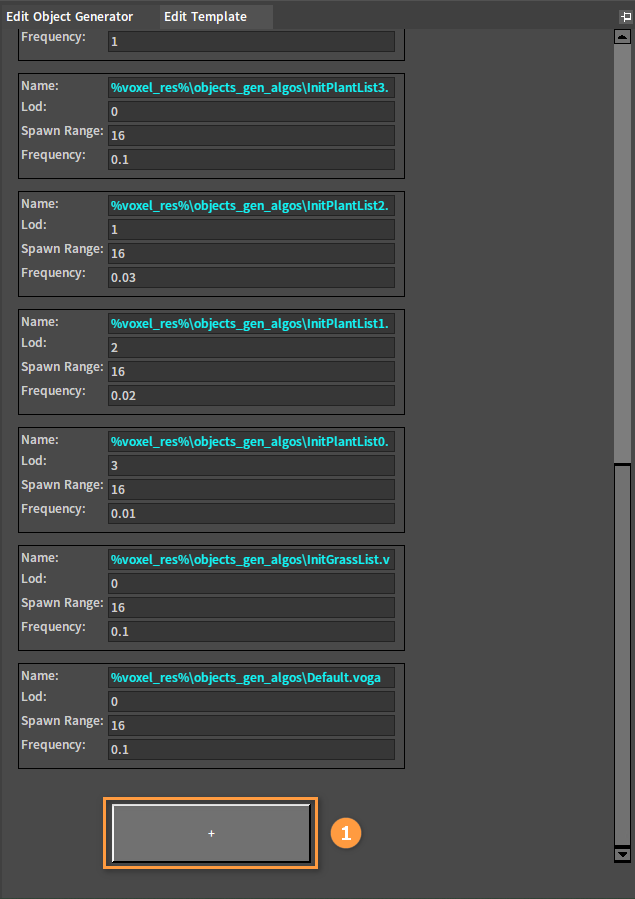
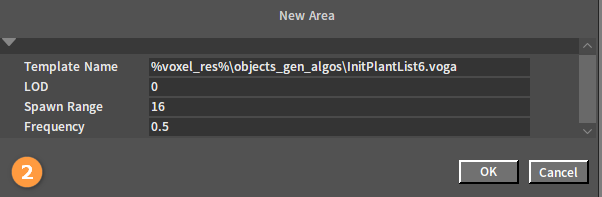
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Template Name | Template name. |
| LOD | LOD level that the foliage is generated on. |
| Spawn Range | The spawn range of the distribution template. |
| Frequency | Spawn frequency. |
Objects can be added by dragging them from the Object Library into the distribution templates and then modifying their spawn ratios. Click the Delete button in the upper right corner to delete them. The final spawn number will be shown in the upper left corner of each object in the distribution templates.
Editing Objects
Enter the Object Editor by clicking OBJECT in the main interface of the Voxel Editor:

In the Object Editor, objects can be added by dragging a model from the Project panel into a blank space in the Editor.
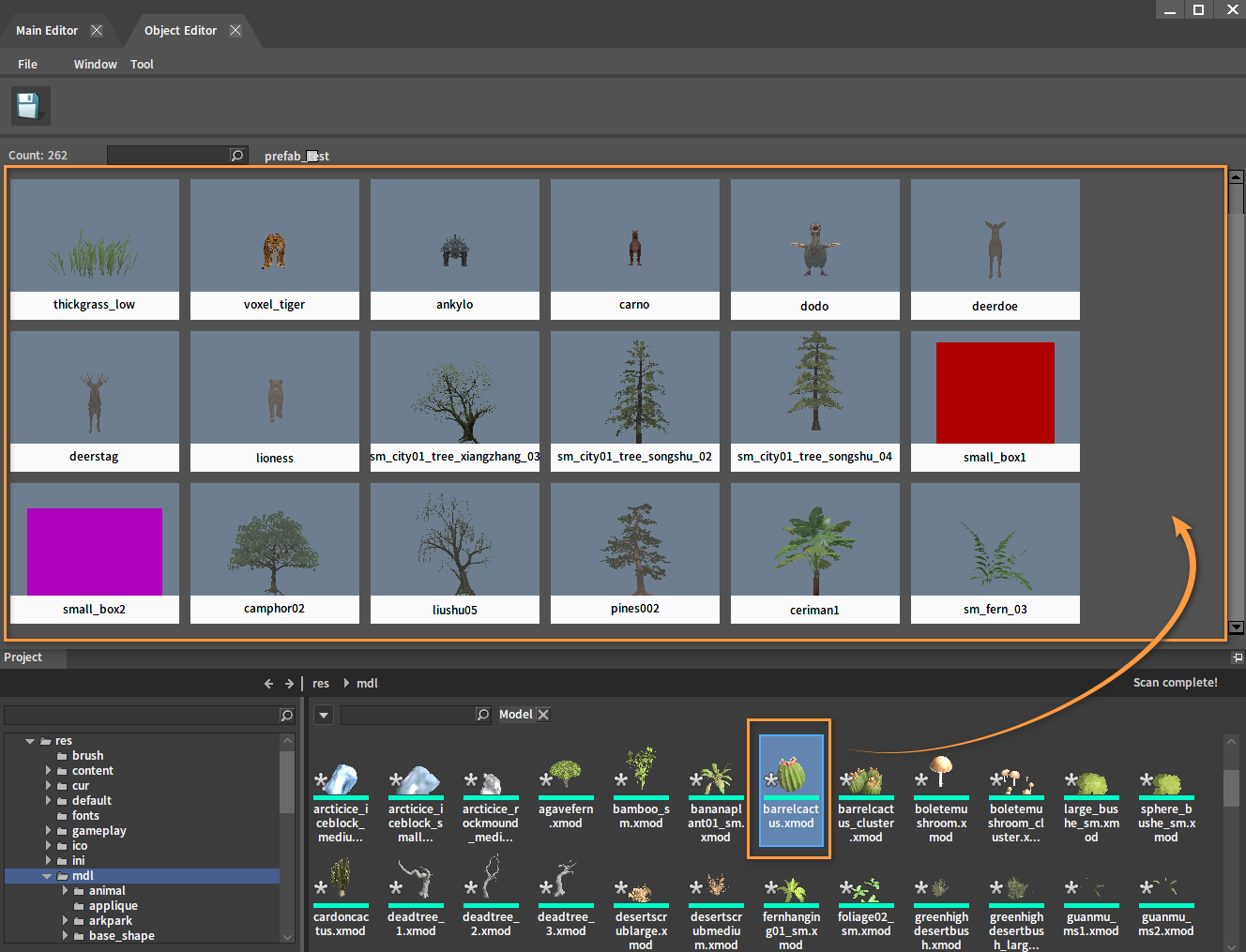
After dragging, select an existing class or create a new class by entering a class name in the pop-up window. Then manage the newly added objects by classes.
Select an existing class:
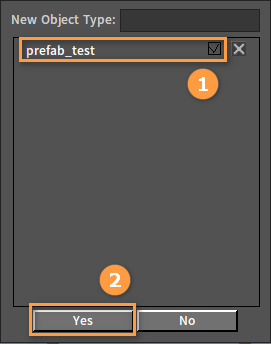
Create a new class:
Existing classes can also be deleted here.
Double-click any object in the Object Library to enter its editing interface. The model can be modified here.
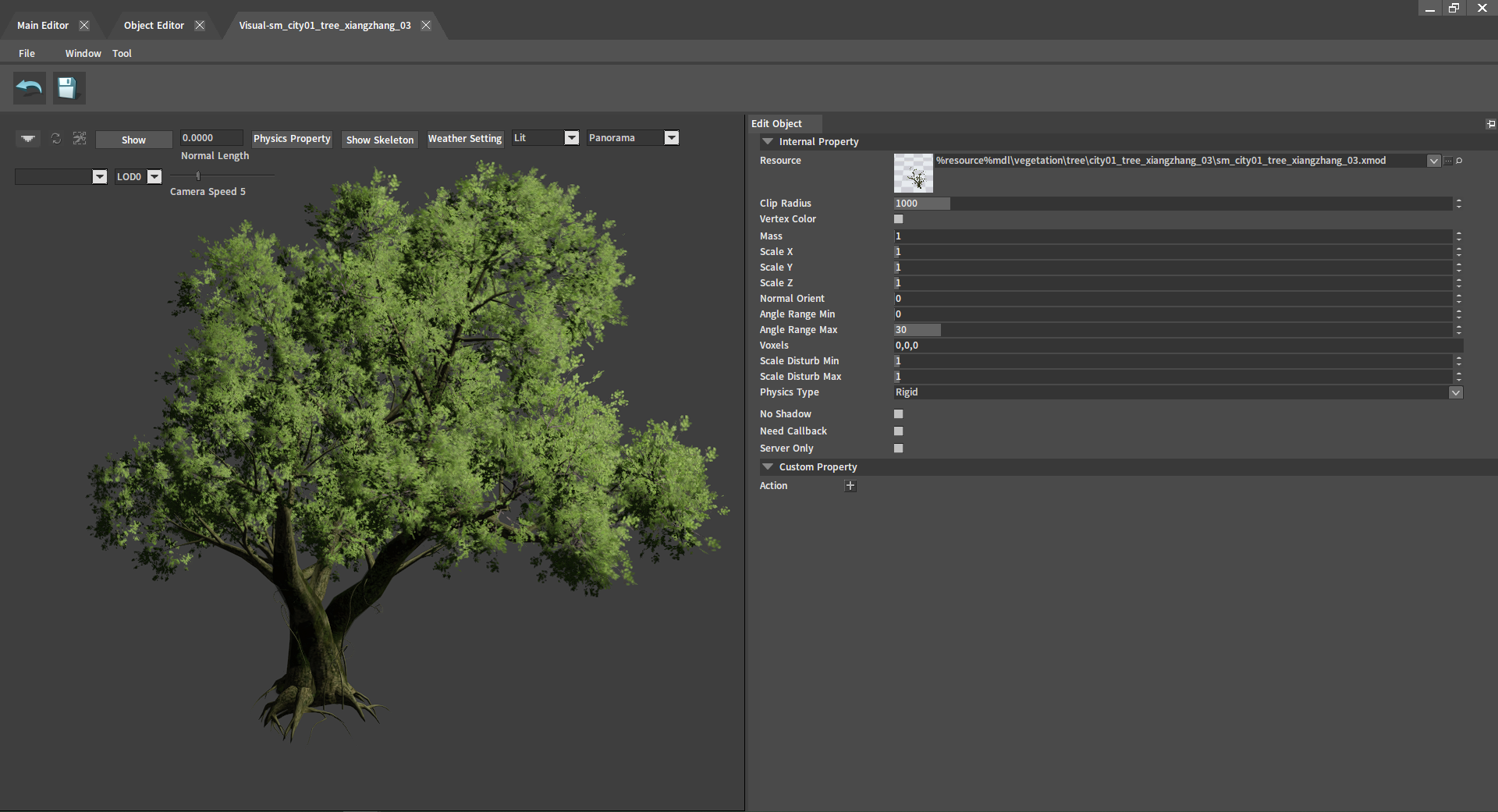
| Setting | Property | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Property | Resource | Select resource. |
| Clip Radius | Clip radius. | |
| Vertex Color | Vertex color. | |
| Mass | Mass. | |
| Scale X | Scale in the X-axis direction. | |
| Scale Y | Scale in the Y-axis direction. | |
| Scale Z | Scale in the Z-axis direction. | |
| Normal Direction | Determine whether the model grows along the normal direction. | |
| Angle Range Min | The threshold for the minimum angle change of objects after random generation. | |
| Angle Range Max | The threshold for the maximum angle change of objects after random generation. | |
| Voxels | Voxel occupancy point. | |
| Scale Disturb Min | The threshold for minimum volume change of objects after random generation. | |
| Scale Disturb Max | The threshold for maximum volume change of objects after random generation. | |
| Physics Type | Select the physical type of the object. | |
| No Shadow | Cancel the display of the shadow effect of the object. | |
| Need Callback | Whether need to receive callbacks for implementing logic features such as creating NPC triggers. | |
| Server Only | Only read by the server, used to implement server logic features. | |
| Custom Property | Action | Used to create some user-defined properties of the object. |
Placing Planets and Planetary Rings in the Level
Placing Planets in the Level
Open the directory res\ter in the Project panel, where the created planets and planetary rings are stored. Select the planet voxel_manager.vter and drag it into the Level.
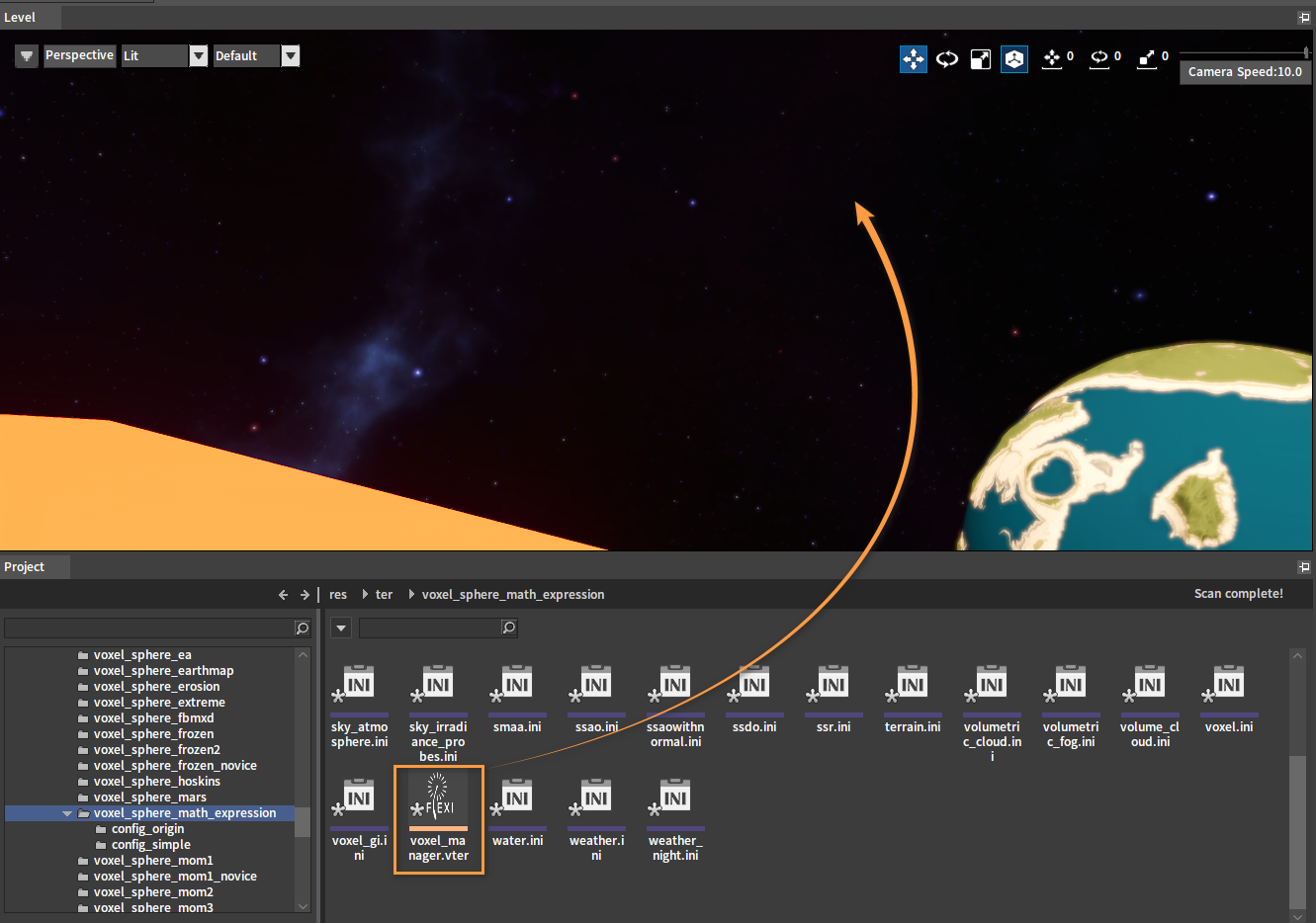
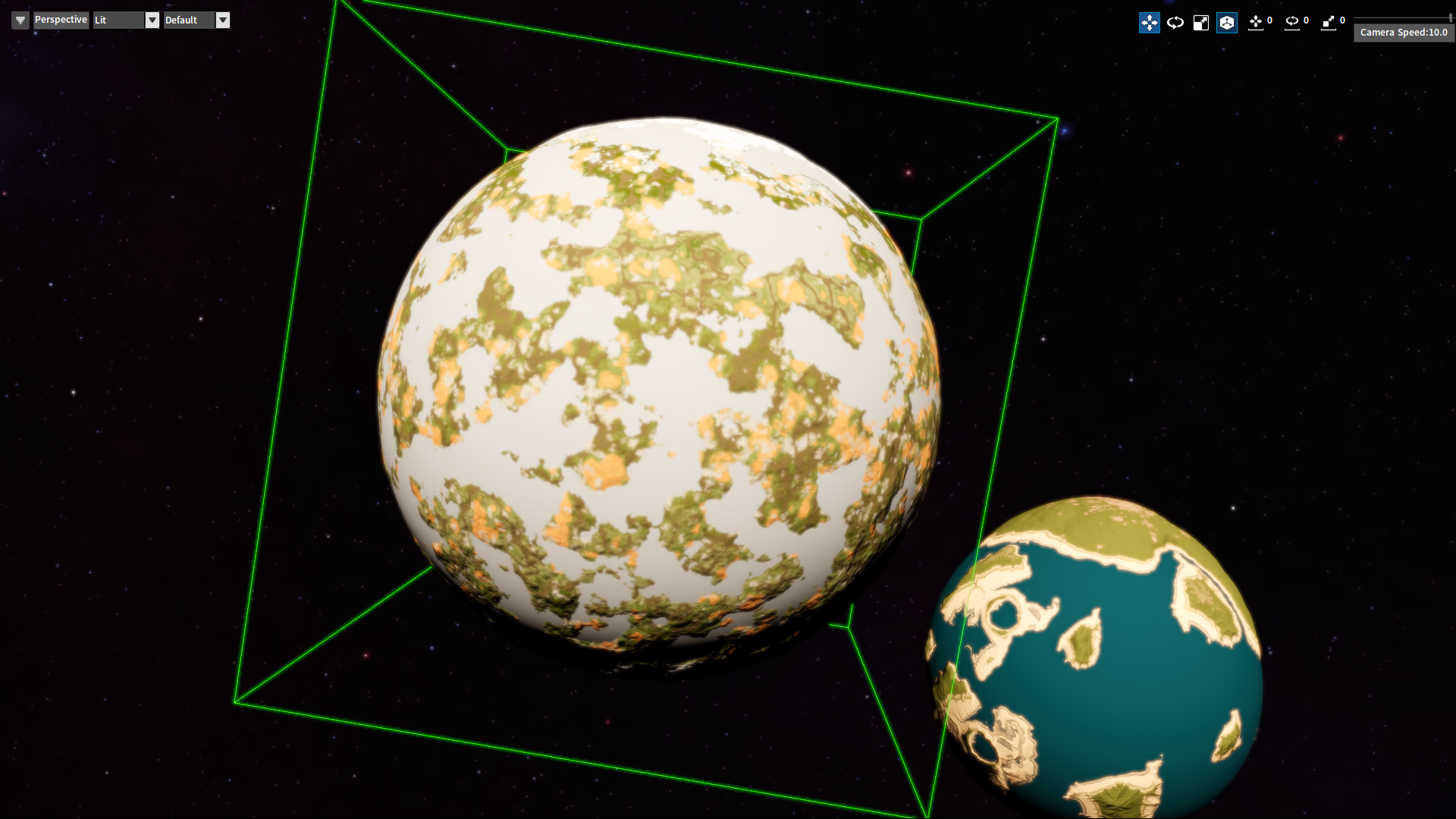
Ecological details on the planet can be seen by pushing in the camera.

Placing Planetary Rings in the Level
Open the directory res\ter in the Project panel, where the created planets and planetary rings are stored. Select the planetary ring voxel_manager.vter and drag it into the Level.
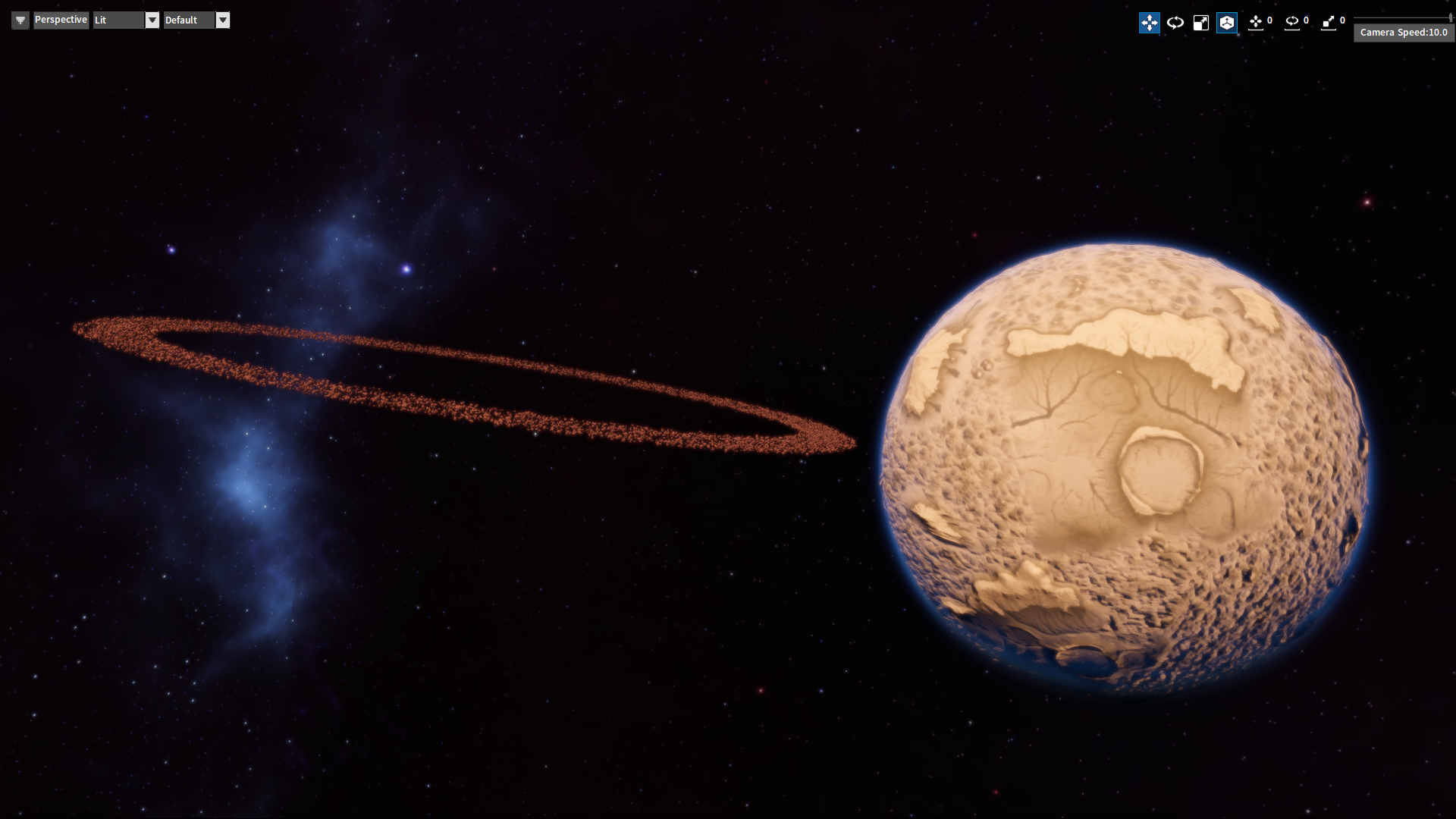
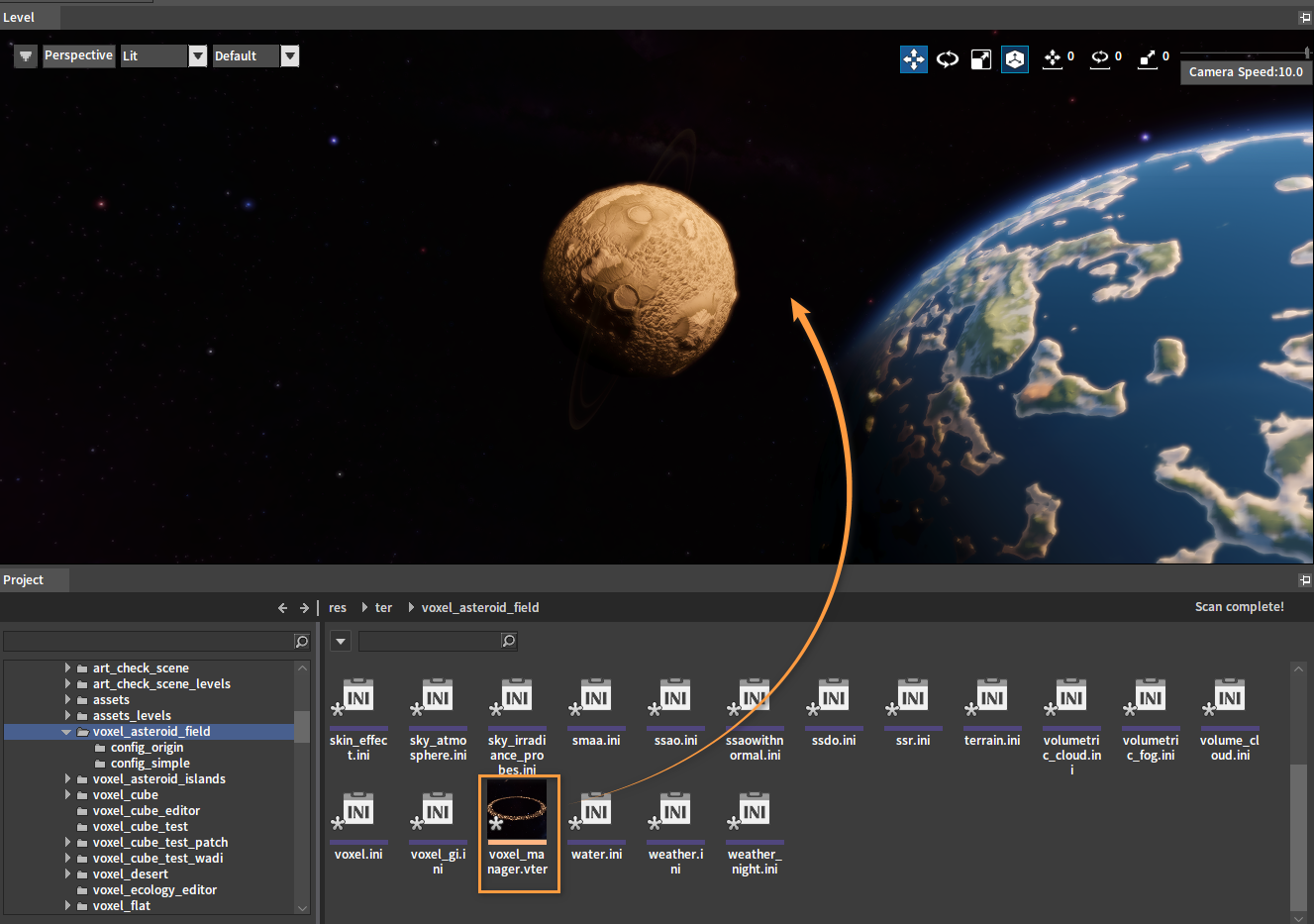

Combining Planets and Planetary Rings
Set the position of the planetary ring to be the same as that of the planet to combine.
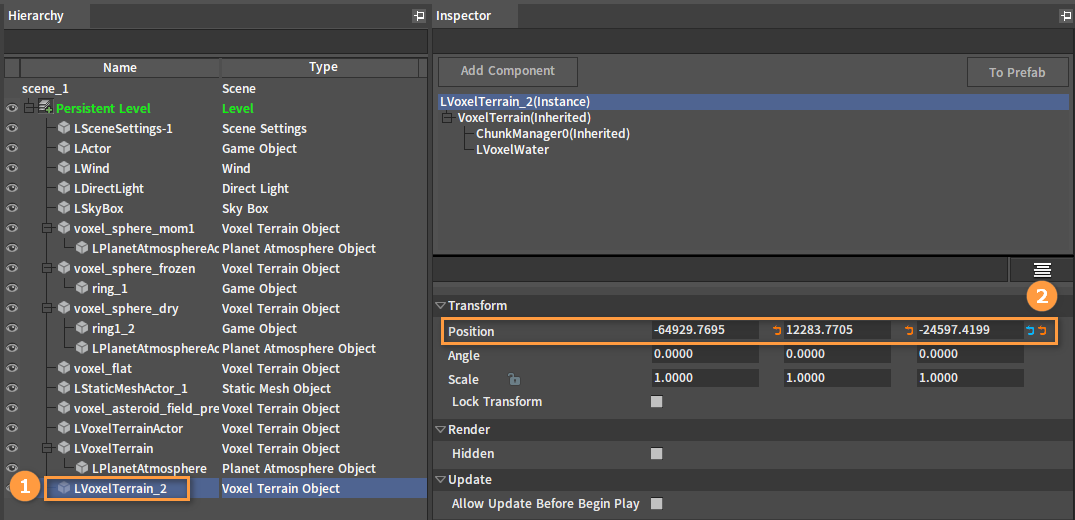
The combined effect is shown below:
