Coding Standards
C/C++ Coding Standards
General standards:
Keep a uniform way of program writing, and Personal Style is Not recommended.
Sign only in the description section at the beginning of the file.
Try not to use abbreviations for naming functions and properties in the interface section.
Each line of the program should be controlled within 80 bytes.
Memory management:
In order to detect the memory leak and secure cross-module memory references, the following methods can be used to allocate and free the memory:
Allocate and free uninitialized memory:
CORE_ALLOCandCORE_FREEGenerate and delete objects:
CORE_NEWandCORE_DELETEIf there is a memory leak, the system will generate a memory leak log (mem_leak.log) in the run directory when it exits, which records detailed information on the memory leak.
Supplementary:
Symbol Description:
____means Tab
▲means Space
Variable definitions
Data Member Local Variable Style I Local Variable Style II bool▲m_bLoop; bool▲bLoop▲=▲false; bool▲loop▲=▲false; int▲m_nTotalSize; int▲nTotalSize▲=▲0; int▲total_size▲=▲0; char▲m_strFileName[32]; char▲strFileName[32]; char▲file_name[32]; char*▲m_strFileName; char*▲pstrFileName▲=▲NULL; char*▲file_name▲=▲NULL; float▲m_fTotalSeconds; float▲fTotalSeconds▲=▲0.0f float▲total_seconds▲=▲0.0f double▲m_dTotalSeconds; double▲dTotalSeconds▲=▲0.0 double▲total_seconds▲=▲0.0 D3DXVECTOR3▲m_vPos; D3DXVECTOR3▲vPos(0.0f,▲0.0f,▲0.0f); D3DXVECTOR3▲pos(0.0f,▲0.0f,▲0.0f); D3DXMATRIX▲m_mtxWorld; D3DXMATRIX▲mtxWorld; D3DXMATRIX▲world; IEntity*▲m_pEntity; IEntity*▲pEntity▲=▲NULL; Operators
Keep one space before and after the operator, e.g.
int▲a▲=▲b▲+▲c;Wrapping
When a wrapping is encountered, the operator should be on the next line, e.g.
int▲a▲=▲xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx▲+▲xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx▲
____+▲xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx;
if▲((xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx)▲&&▲(xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx)▲
____&&▲(xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx)▲&&▲(xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx))
{
}
else▲if▲()
{
}Wrapping format at the declaration:
//▲Read custom material data
return_string▲GetCustomMaterialValue(const▲char*▲mat_name,▲
____const▲char*▲key);Wrapping format at the definition:
return_string▲Model::GetCustomMaterialValue(const▲char*▲mat_name,▲
____const▲char*▲key)When dealing with code segments with different contents, separate them with (null string) blank lines.
Comments
1)Single line comments followed by a space, e.g.
//▲Comment2)Comments and declarations for the Get Type properties
///▲readonly: string Name
///▲\brief Name
DECLARE_PROPERTY_GET(const▲char*,▲Model,▲Name,▲GetName);
//▲Name
const▲char*▲GetName()▲const;3)Comments and declarations for the Get Type and the Set Type properties
///▲property: bool AsyncLoad
///▲\brief Whether to load asynchronously
DECLARE_PROPERTY(bool,▲Model,▲AsyncLoad,▲GetAsyncLoad,▲SetAsyncLoad);
//▲Whether to load asynchronously
void▲SetAsyncLoad(bool▲value);
bool▲GetAsyncLoad()▲const;4)Comments and declarations for the fixed-number parameter method
///▲method: bool SetSpeed(float speed)
///▲\brief Set the playback speed
///▲\param speed Speed (normal speed is 1.0)
DECLARE_METHOD_1(bool,▲Model,▲SetSpeed,▲float);
//▲Set the playback speed
bool▲SetSpeed(float▲speed);5)Comments and declarations for the unfixed-number parameter method
///▲method: [x, y, z] GetHelperPosition(string group, string name)
///▲\brief Get the current position of the auxiliary point
///▲\param group Auxiliary point group name
///▲\param name Auxiliary point name
DECLARE_METHOD_N(Model,▲GetHelperPosition);
//▲Get the current position of the auxiliary point
void▲GetHelperPosition(const▲IVarList&▲args,▲IVarList&▲result);6)Comments and declarations for entity method that returns the list
///▲method: table GetHelperNameList()
///▲\brief Get the name list of all auxiliary points
DECLARE_METHOD_T(Model,▲GetHelperNameList);
//▲Get the name list of auxiliary points
void▲GetHelperNameList(const▲IVarList&▲args,▲IVarList&▲result);Pay attention to your Tab key, set up your editing tools to unify with the project, and pay attention to neat typography.
Script Coding Standards
In the UI Editor, the automatically generated function names can be slightly modified, but the keywords cannot be deleted.
Examples that meet the requirements:
xxx_btn_click;xxx_checked_changed;xxx_edit_lost_focus;xxx_edit_dragxxx means keywords used for description such as functions, properties, etc.
Format of spaces after keywords
There should be one space after
ifwhileforetc.Operators
Keep one space before and after the operator, e.g.
local▲a▲=▲b▲+▲cWhen there is a wrapping, the operator should be on the next line, e.g.
local▲a▲=▲xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx▲+▲xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx▲
+▲xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
if▲(xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx)▲and▲(xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx)▲
and▲(xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx)▲and▲(xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx)▲then
--......
endThe code segment defining/declaring a variable should be a separate paragraph with a blank line after it.
local▲x▲=▲1
local▲y▲=▲1
if▲......When handling code segments with different contents, separate them with blank lines.
No spaces after script comments, e.g.
--Comment;Different from C/C++ comments, there should be a space after the comment, e.g.//▲CommentProperty and variable definitions:
Variable names defined by scripts must be in lower case (except for defining constants, where all characters are usually capitalized).
Custom property names of entities use lower-case letters separated by underscores, e.g.,
prop_name, thus distinguishing them from the entity's internal properties.When the performance impact is not significant, use
nx_callto call non-asynchronous functions in other script files, and try not to userequireto include other script files, as this will affect the reloading of scripts after modifications.Write enough comments, as the script program may change frequently.
No semicolons (;) allowed.
Pay attention to your Tab key, set up your editing tools to unify with the project, and pay attention to neat typography.
The length of the code line should not exceed 80 characters (the Engine code requires no more than 80 characters).
Be sure to test the code before submitting it, compare it with the one before modification, and check in passing whether it is neatly laid out, streamlined, etc.
The global interface entity name must conform to: descriptive keywords + form
E.g.
nx_value("xxx_form")ornx_value("xxx_xxx_form")etc.Avoid entity leak
1)When creating a temporary entity, be careful to destroy it in all
returnplaces, such as:ArrayList,IniDocument,XmlDocumentof tool class.2)When creating an
ArrayListentity withnx_create, remember to write the second parameter:local▲xxx▲=▲nx_create("ArrayList",▲"xxx_xxx_xxx")3)The global entity must be destroyed before exiting the system.
In the above way, it is easier to find entity leaks.
Script Coding Instructions
Calling the nx_current() interface in the same script file may return different results. The example is shown below:
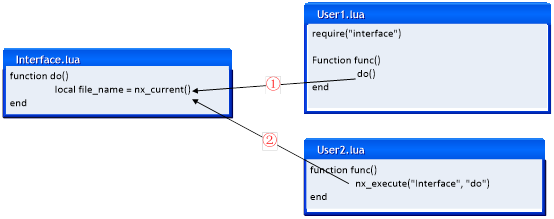
Notes:
When calling ①, the return value of nx_current() is "User1.lua", please note that User1.lua contains the header file of the interface Interface.lua.
When calling ②, the return value of nx_current() is "Interface.lua".